Discover the best strategies and practices for protecting sensitive data in cloud computing environments. Learn about encryption, access controls, backup solutions, and more. In today’s digital age where data breaches and cyber threats are prevalent, Cloud service data protection plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and confidentiality of valuable information stored in the cloud. By implementing robust security measures and adhering to best practices, organizations can mitigate risks and safeguard their data effectively.

Understanding Cloud Service Data Protection
In the realm of cloud computing, data protection encompasses a comprehensive set of strategies aimed at safeguarding sensitive information within cloud environments. This includes shielding data from unauthorized access, breaches, loss, and other cybersecurity risks. Cloud service providers furnish an array of protective tools like encryption, access controls, and backup and recovery systems to fortify data security. However, organizations must augment these measures with their own data protection protocols to fortify their defenses.
Maximizing Data Protection with Encryption in the Cloud
Understanding Encryption for Enhanced Data Security
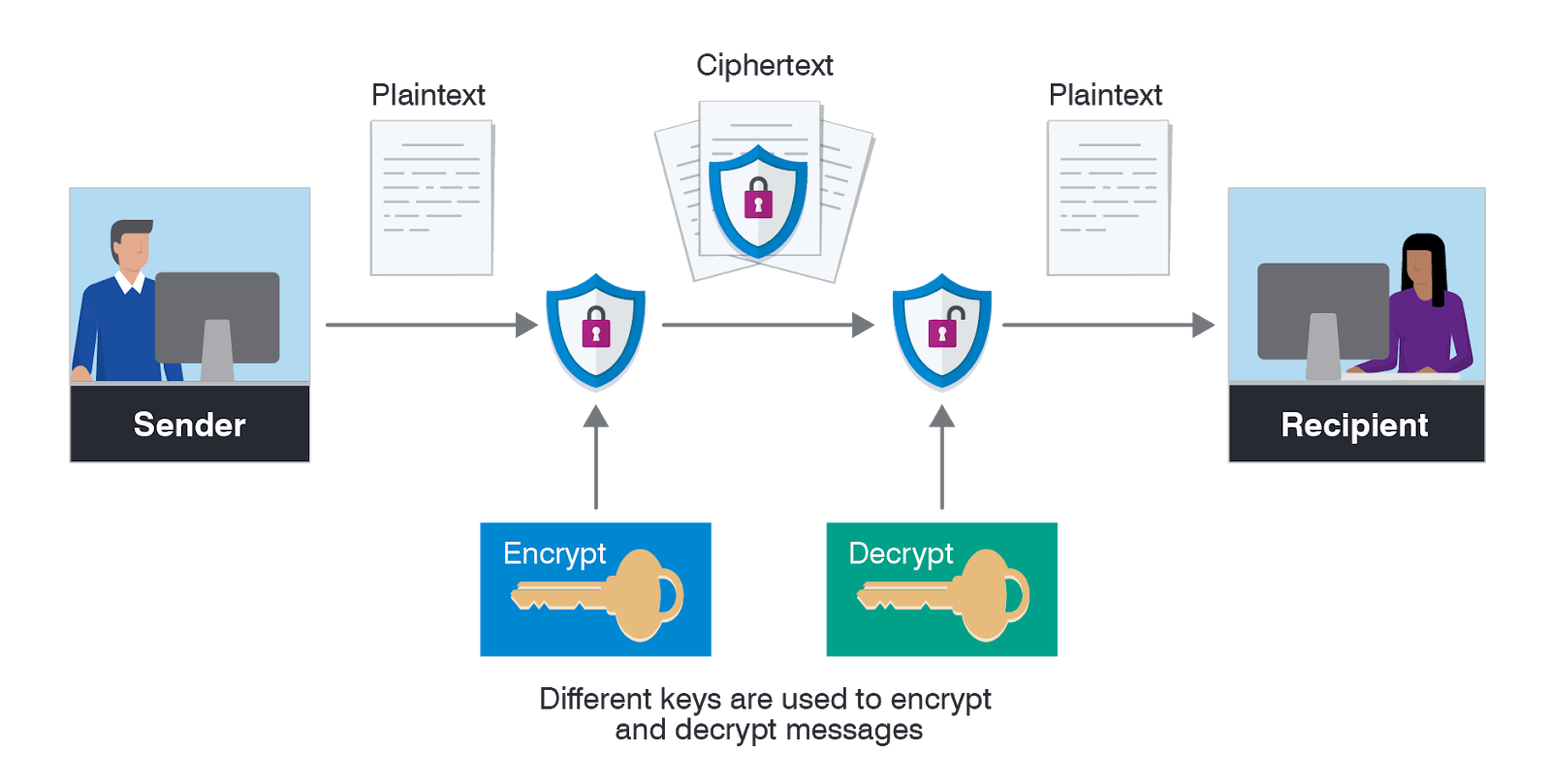
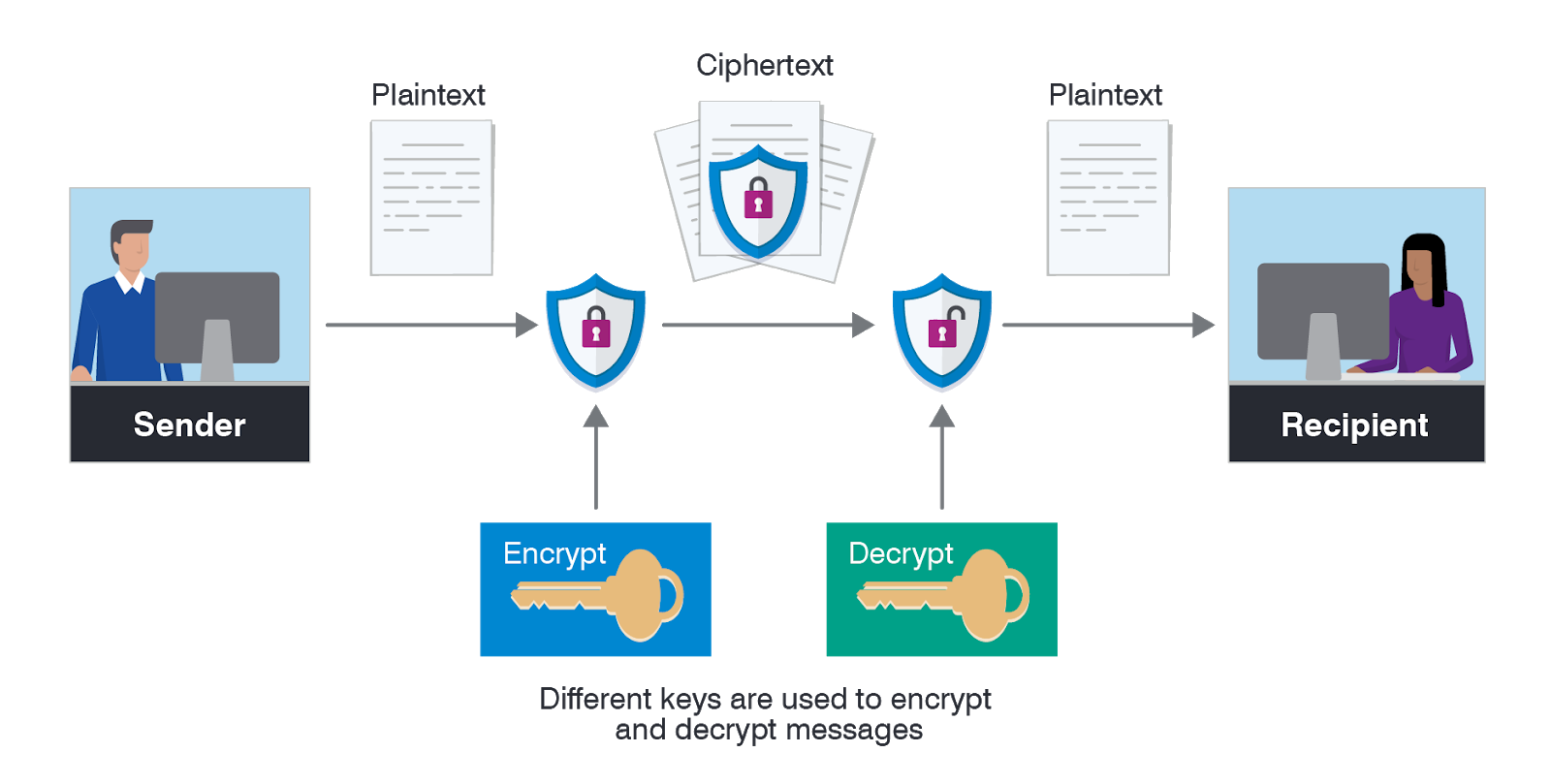
Encryption stands as a cornerstone in safeguarding sensitive information within cloud environments. By transforming data into an incomprehensible format through advanced encryption algorithms, like AES, data remains secure from unauthorized access.
Leveraging Cloud Provider Encryption Services
Cloud service providers ensure data security through encryption at rest, shielding stored information, and encryption in transit, securing data during transmission. This dual encryption layer fortifies the data protection mechanism in the cloud.
Strengthening Security with Client-Side Encryption
To bolster protection, organizations can opt for client-side encryption, enabling data to be encrypted on the user’s end before transmission to the cloud. This extra encryption layer heightens security and ensures data confidentiality at all stages.
Secure Management of Encryption Keys
Managing encryption keys is critical to thwart decryption attempts. By securely storing and rotating encryption keys, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and maintain the integrity of their encrypted data, thereby upholding cloud service data protection.

Implementing Robust Access Controls for Enhanced Cloud Data Protection
Access controls are paramount in restricting unauthorized access to sensitive data stored in the cloud. Cloud providers offer sophisticated tools like role-based access control (RBAC) and identity and access management (IAM) systems. By setting stringent access policies and regularly reviewing user permissions, organizations can maintain data integrity and confidentiality effectively. Additionally, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO) adds extra layers of security to access controls, bolstering overall data protection measures.
Enhancing Data Privacy with Data Masking and Anonymization
Data masking and anonymization techniques serve as vital shields safeguarding sensitive personal data from falling into unauthorized hands. While data masking ingeniously substitutes confidential information with fabricated values, anonymization meticulously alters or eliminates personal identifiers to thwart re-identification attempts.
Cloud service providers extend a helping hand by furnishing cutting-edge data masking and anonymization tools, empowering organizations to seamlessly adhere to stringent privacy regulations and fortify their data protection mechanisms.
Striking a delicate equilibrium between fortifying data privacy and preserving data utility is paramount for organizations diving into the realm of data masking and anonymization. Careful consideration of this balance ensures both data security and operational efficiency are harmoniously maintained.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Regulations in Cloud Data Protection
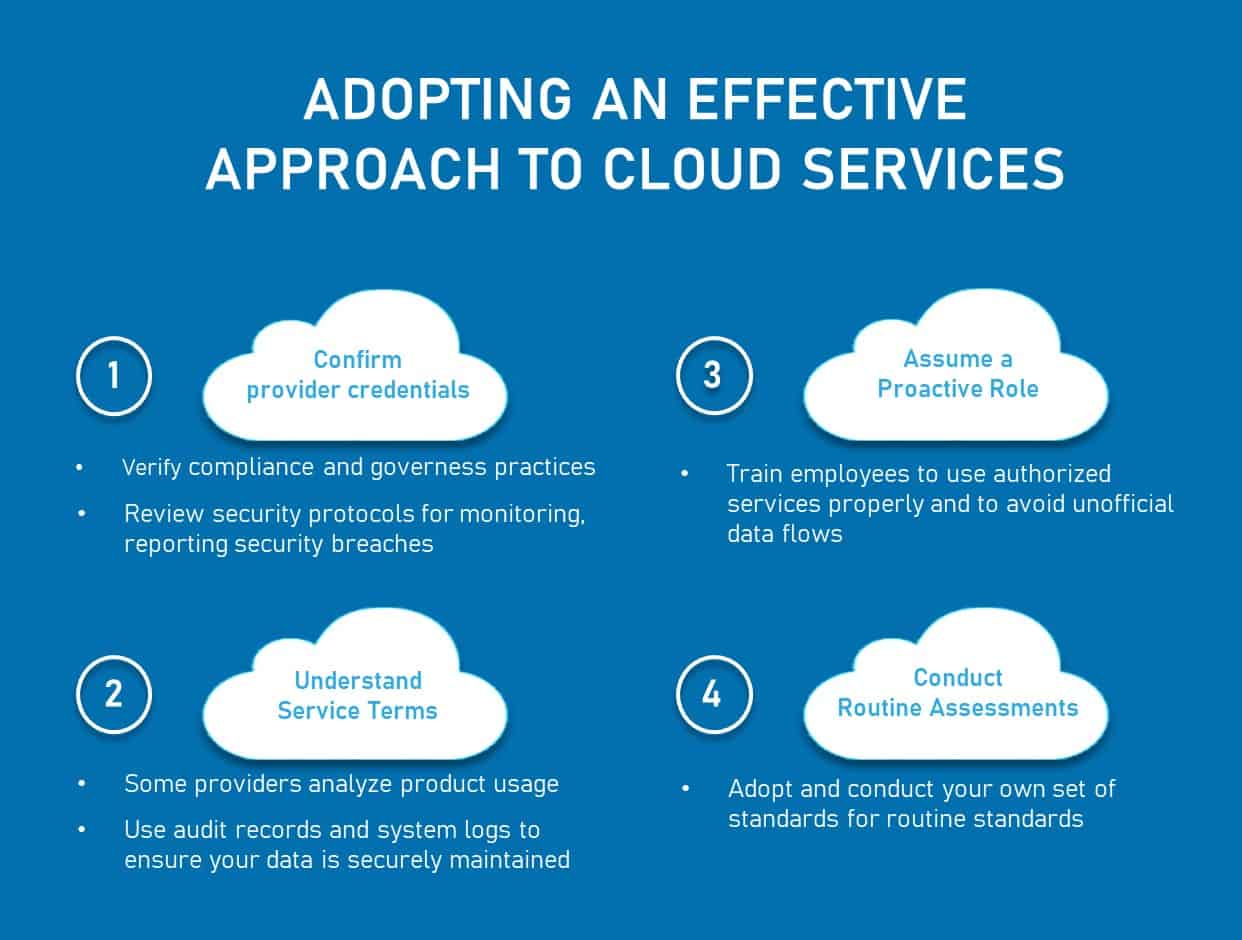
Cloud service data protection is closely tied to adherence to stringent industry regulations and standards. Organizations entrusting their data to cloud service providers must guarantee that these providers meet their specific compliance requirements. Key frameworks such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR, and NIST outline crucial guidelines for data protection in the cloud.
Regular auditing of cloud providers is vital to validate compliance with established regulations and to promptly address any identified gaps. By staying proactive in compliance assessments, organizations can uphold the integrity and security of their data stored in the cloud, ensuring robust protection against potential breaches and vulnerabilities.

Best Practices for Cloud Service Data Protection
Implementing a Comprehensive Data Protection Strategy
To ensure robust Cloud service data protection, organizations must tailor their strategy to match risk tolerance and compliance needs. This involves assessing data sensitivity levels, implementing encryption protocols, and defining access controls. By aligning protection measures with specific requirements, data security can be greatly enhanced.
Regular Review and Updates of Data Protection Measures
Staying ahead of evolving threats and regulatory shifts is critical in cloud data protection. Regularly audit data security infrastructure, update encryption methods, and revise access permissions to adapt to changing environments. By proactively maintaining protective measures, organizations can effectively safeguard sensitive information.
Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Conducting periodic security audits and penetration tests is essential for identifying vulnerabilities. These tests simulate real-world attack scenarios, allowing organizations to discover weak points in their data protection systems. By addressing these weaknesses promptly, potential breaches can be prevented, ensuring robust Cloud service data protection.
Employee Training on Data Protection Best Practices
Human error and insider threats pose significant risks to cloud data security. Educating employees on data protection protocols, safe data handling practices, and recognizing social engineering tactics can fortify the human element of cybersecurity. By promoting a culture of data security awareness, organizations can reduce the likelihood of data breaches and unauthorized access.