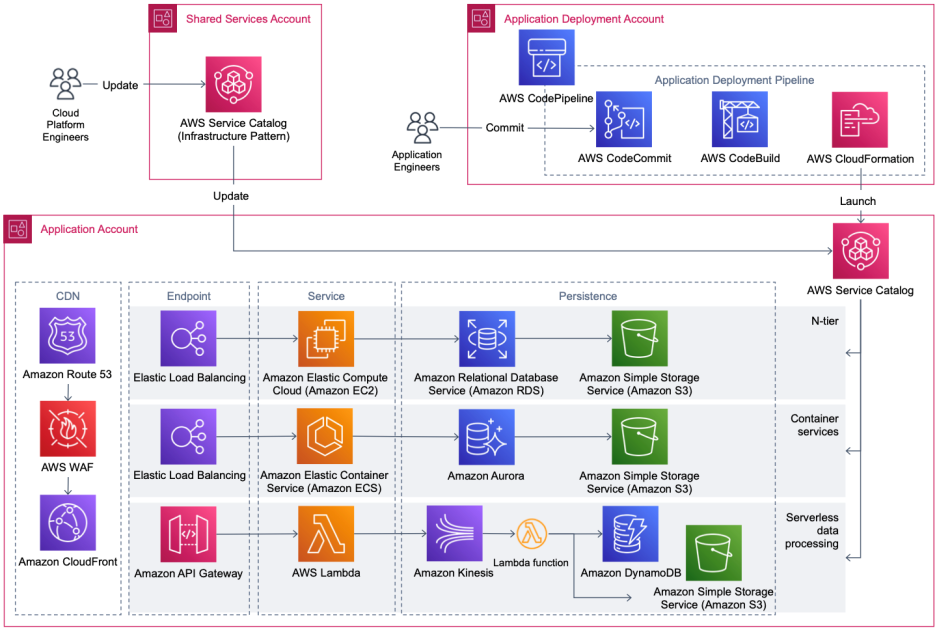
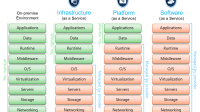
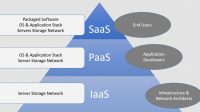
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of cloud service catalogs, essential tools for businesses looking to streamline their IT services. Cloud service catalogs act as a centralized hub for all available services, offering organizations a clear overview of their IT resources. From defining the key components to exploring the various types and detailed steps for creation and management, this guide covers it all. Stay tuned to uncover the benefits, challenges, and future trends shaping the landscape of cloud service catalogs. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced professional, this guide aims to enhance your understanding of cloud service catalogs and their pivotal role in modern IT operations.
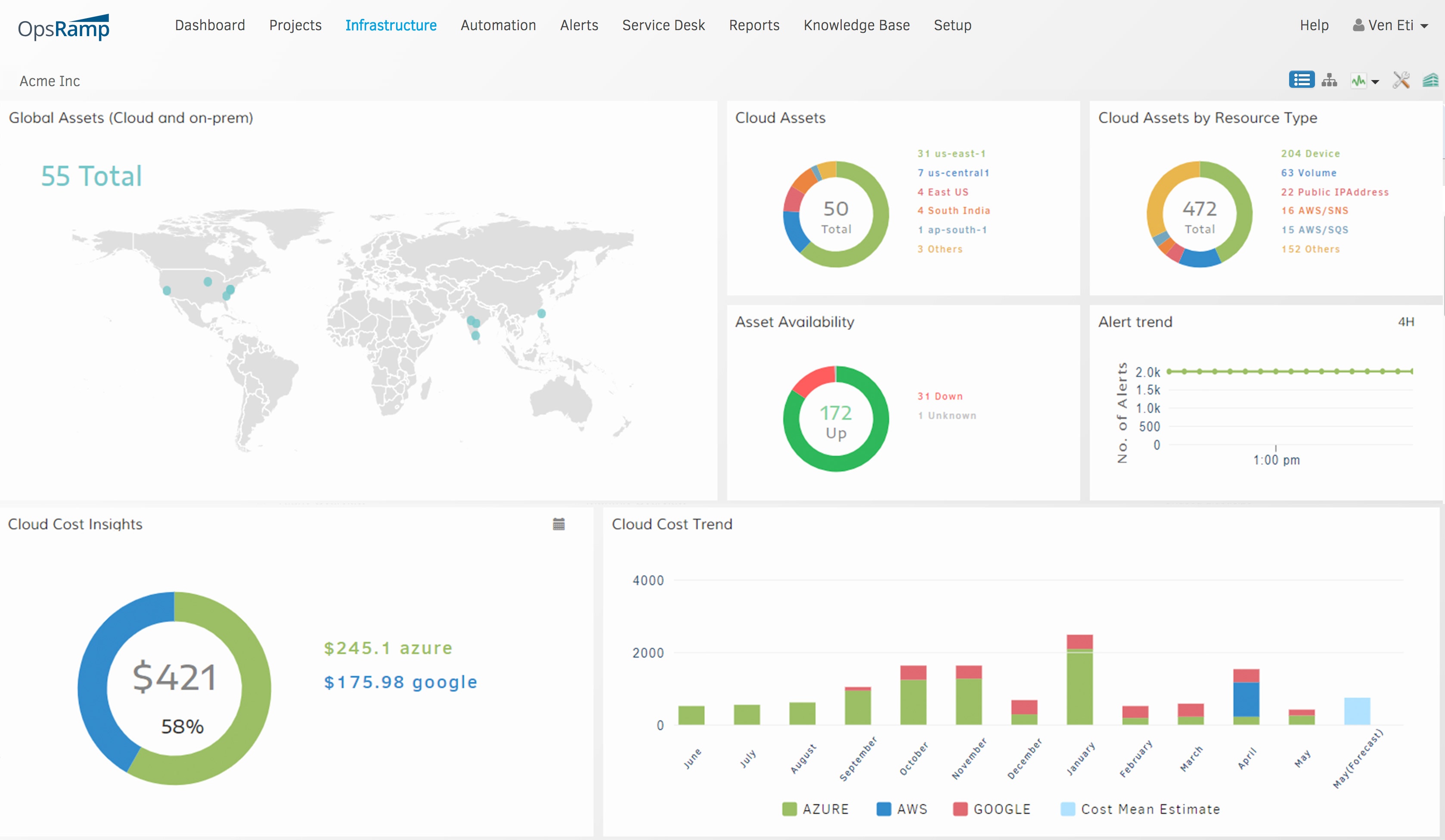
Understanding Cloud Service Catalogs
Definition and Purpose of a Cloud Service Catalog
A cloud service catalog is a centralized database that contains information about all available IT services within an organization. It serves as a one-stop-shop for IT resources, providing a clear overview of what services are offered, their descriptions, and how they can be accessed. This tool helps streamline IT service management and facilitates communication between IT teams and business stakeholders.
Benefits of Implementing a Cloud Service Catalog
Implementing a cloud service catalog offers numerous benefits, including enhanced transparency, improved service delivery, better resource utilization, and increased efficiency. By having a centralized repository of services, organizations can standardize service offerings, reduce duplication, and ensure alignment between IT services and business objectives. Moreover, it enables users to easily request and access services through a user-friendly interface.
Key Components and Features of a Cloud Service Catalog
A comprehensive cloud service catalog typically includes service descriptions, pricing information, service level agreements (SLAs), ordering processes, service dependencies, and relevant documentation. It may also incorporate user feedback mechanisms, self-service capabilities, and integration with other IT service management tools. The catalog should be regularly updated to reflect changes in services and ensure accuracy for users.
Best Practices for Creating and Managing a Cloud Service Catalog
To create and manage a successful cloud service catalog, organizations should involve key stakeholders from IT and business units, define clear taxonomy and categorization for services, establish governance processes for catalog maintenance, and regularly review and update service information. It’s crucial to monitor service performance, gather feedback from users, and continuously improve the catalog’s usability and relevance.

Exploring the Diverse Types of Cloud Service Catalogs
Internal vs. External Cloud Service Catalogs
Internal catalogs are tailored for an organization’s internal IT services, while external catalogs cater to services provided by external vendors. Internal catalogs offer better customization for specific business needs, whereas external catalogs provide access to a broader range of specialized services.
Static vs. Dynamic Cloud Service Catalogs
Static catalogs feature fixed service offerings, ideal for stable environments. In contrast, dynamic catalogs adapt to changing demands by allowing real-time updates and modifications to service listings, ensuring flexibility and agility in service delivery.
Open vs. Closed Cloud Service Catalogs
Open catalogs provide visibility across the organization, promoting collaboration and transparency in service consumption. Closed catalogs restrict access to specific user groups, enhancing security and control over service provisioning.
Considerations for Choosing the Right Type of Cloud Service Catalog
When selecting a cloud service catalog type, factors like organizational requirements, scalability, security preferences, and collaboration needs must be assessed. Tailoring the catalog type to align with business objectives ensures optimal utilization and efficiency in service management.
Embracing the diverse types of cloud service catalogs empowers businesses to align their IT services effectively with organizational goals and operational requirements. By understanding the distinctions between internal and external, static and dynamic, open and closed catalogs, organizations can make informed decisions to optimize service delivery, enhance collaboration, and ensure security in their cloud service catalog implementations.

Crafting a Robust Cloud Service Catalog
Steps for Creating a Cloud Service Catalog
Creating a comprehensive cloud service catalog involves initial steps such as identifying the services to be included, documenting service details, defining service levels, and determining pricing structures. It is crucial to collaborate with stakeholders to align catalog offerings with business objectives, ensuring relevance and value.
Defining Service Offerings, Attributes, and Approval Processes
To enhance user experience, clearly define each service offering with detailed descriptions, attributes, and associated benefits. Implement a structured approval process to validate new service additions or modifications, maintaining catalog accuracy and relevance. This step ensures consistency and transparency in service delivery.
Integrating with Cloud Management Platforms and Tools
Seamless integration with cloud management platforms and tools optimizes catalog accessibility and usability. By leveraging automation and self-service capabilities, organizations streamline service request processes and empower users to explore and select services efficiently. This integration enhances operational efficiency and resource utilization.
Establishing Governance and Compliance Requirements
Incorporating governance and compliance considerations into the catalog creation process is essential to meet industry standards and regulatory requirements. Define policies, access controls, and security measures within the catalog framework to uphold data protection, risk management, and overall IT governance. This ensures a secure and compliant service environment.

Mastering the Art of Managing a Cloud Service Catalog
Maintaining and Updating Service Offerings
Managing a cloud service catalog involves ensuring that all service offerings are current and relevant. Regular updates are essential to reflect new services, changes, and retirements accurately. By maintaining a dynamic catalog, organizations can provide users with up-to-date information on available IT services, fostering efficiency and alignment with business objectives.
Monitoring Usage and Performance
Effective management includes monitoring service usage and performance metrics within the catalog. By analyzing usage patterns and performance indicators, organizations can optimize resource allocation, identify underutilized services, and refine service quality. This proactive approach enhances decision-making, scalability, and overall user satisfaction with the cloud service catalog.
Enforcing Governance Policies and Approvals
To maintain operational integrity, cloud service catalogs require stringent governance policies and approval mechanisms. By enforcing access controls, authorization procedures, and compliance checks, organizations can safeguard against unauthorized usage, mitigate risks, and ensure alignment with regulatory requirements. This systematic approach strengthens security, control, and accountability in managing the catalog.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards
Compliance with industry standards is pivotal in managing a cloud service catalog. Organizations must adhere to regulations, certifications, and best practices to uphold data integrity, security, and privacy. By aligning the catalog with industry standards, businesses can build trust, demonstrate reliability, and mitigate legal or reputational risks associated with non-compliance.

Unlocking the Value: Benefits of Using a Cloud Service Catalog
Improved Visibility and Control Over Cloud Services
Cloud service catalogs provide a comprehensive view of available services, empowering organizations with visibility into their IT resources. By centralizing services, businesses gain better control over their cloud assets, enabling efficient allocation and management of resources, enhancing operational transparency.
Increased Efficiency and Cost Optimization
Through a cloud service catalog, businesses can streamline service requests and automate provisioning processes, leading to increased operational efficiency. This optimization not only accelerates service delivery but also aids in cost management by minimizing resource wastage and improving budget allocation through informed decision-making.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
A cloud service catalog enhances security measures by enforcing standardized service configurations and access controls, reducing vulnerabilities. By adhering to predefined service policies, organizations can ensure regulatory compliance and mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access or data breaches, safeguarding sensitive information effectively.
Reduced Risk and Improved Governance
By leveraging a cloud service catalog, businesses can mitigate risks associated with inconsistent service provisioning or ad-hoc deployments. Standardized service offerings and governance protocols ensure compliance with best practices, promoting a structured approach to managing services, reducing operational risks, and enhancing overall governance within the IT infrastructure.

Addressing the Challenges in Implementing a Cloud Service Catalog
Data Integration and Synchronization Issues
Implementing a cloud service catalog often involves integrating data from various sources. Challenges arise in synchronizing this data seamlessly, ensuring accuracy and consistency across the catalog. Compatibility issues, data silos, and differing formats may hinder the smooth integration process, requiring meticulous planning and execution to overcome.
Managing Complexity and Scale
One of the significant challenges in deploying a cloud service catalog is managing the inherent complexities and scale of IT services and resources. As organizations expand their service offerings, catalog management becomes intricate. Balancing agility with governance, while catering to diverse requirements, demands robust catalog structuring and categorization strategies.
Ensuring Adoption and User Buy-In
Successful implementation hinges on user acceptance and engagement. Encouraging adoption among stakeholders, including IT teams and end-users, is vital for maximizing the benefits of a cloud service catalog. Educating users on the catalog’s value, providing training, and incorporating user feedback are crucial steps in ensuring widespread buy-in and utilization.
Continuous Maintenance and Updates
Maintaining a cloud service catalog requires ongoing attention to ensure its relevance and accuracy. Regular updates, incorporating new services, retiring obsolete ones, and revising service details are essential tasks. Balancing agility with stability, organizations must establish efficient processes for continuous catalog maintenance to adapt to evolving business needs and technologies.

Future Trends in Cloud Service Catalogs
Automation and Self-Service Provisioning
The future of cloud service catalogs is moving towards increased automation and self-service provisioning. Organizations are embracing automated workflows to reduce manual interventions, allowing users to request and provision services independently. This trend ensures efficiency, agility, and cost-effectiveness in managing IT resources through streamlined processes within the catalog.
Integration with AI and ML for Intelligent Recommendations
Cloud service catalogs are evolving to leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms for providing intelligent recommendations. By analyzing user behavior and historical data, AI-driven catalogs can suggest suitable services, optimize resource allocation, and enhance user experience. This integration aims to tailor services to individual needs and improve decision-making processes.
Cloud-Native Service Catalogs with Enhanced Capabilities
The future landscape of cloud service catalogs is shifting towards cloud-native architectures with advanced capabilities. Modern catalogs are designed to be more agile, scalable, and flexible, enabling seamless integration with diverse cloud environments. This evolution ensures adaptability to changing business requirements and the ability to cater to a variety of services efficiently.
Role-Based Access and Personalized Experiences
Future cloud service catalogs will focus on providing role-based access and personalized experiences to users. By tailoring service offerings based on individual roles and responsibilities, organizations can enhance user satisfaction, increase productivity, and maintain data security. This trend emphasizes delivering customized services that align with specific user needs and preferences.