Are you looking to delve into the intricate world of cloud service provisioning? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of Cloud service provisioning, including its benefits, various models such as IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, key considerations for selecting a provider, and best practices. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned professional in the IT industry, understanding the nuances of cloud service provisioning is essential in today’s digital landscape. Let’s unravel the complexities and unveil the possibilities that Cloud service provisioning has to offer.

Understanding Cloud Service Provisioning: Unveiling the Power of Cloud Solutions
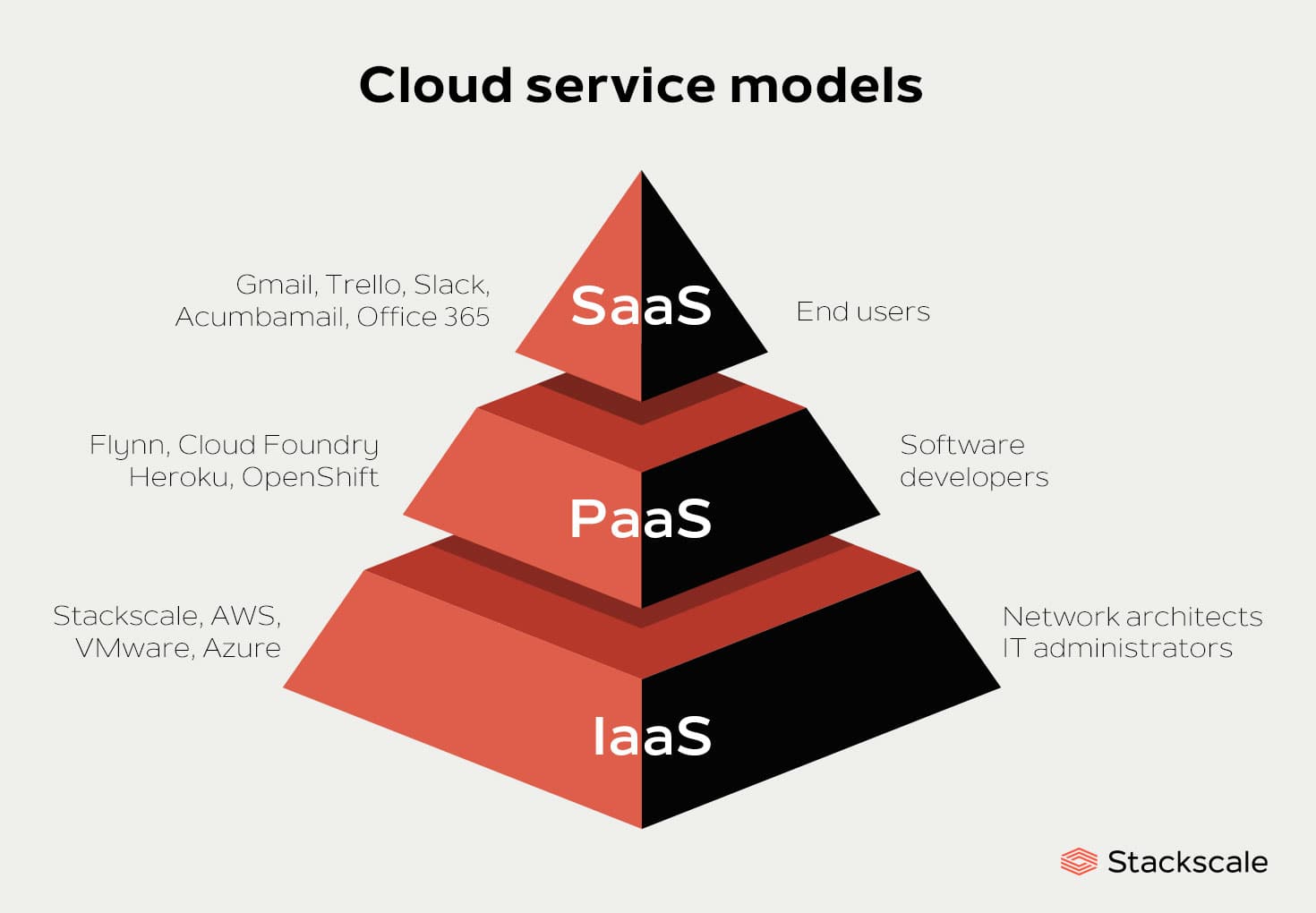
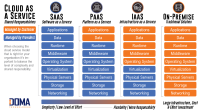
Cloud service provisioning is the method of providing cloud services like infrastructure, platforms, and software over the internet. This approach offers scalability, affordability, and adaptability, presenting an appealing choice for businesses seeking efficiency. The primary cloud service models, namely Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), cater to different levels of service delivery, addressing varied business needs dynamically.
Empowering Businesses with On-Demand Access
Cloud service provisioning revolutionizes how businesses secure resources by enabling them to procure services on demand. This transformative approach diminishes the necessity for extensive in-house infrastructure, allowing companies to leverage external, scalable resources efficiently. The ability to access resources flexibly aligns with the dynamic requirements of modern enterprises, promoting operational agility and cost optimization.
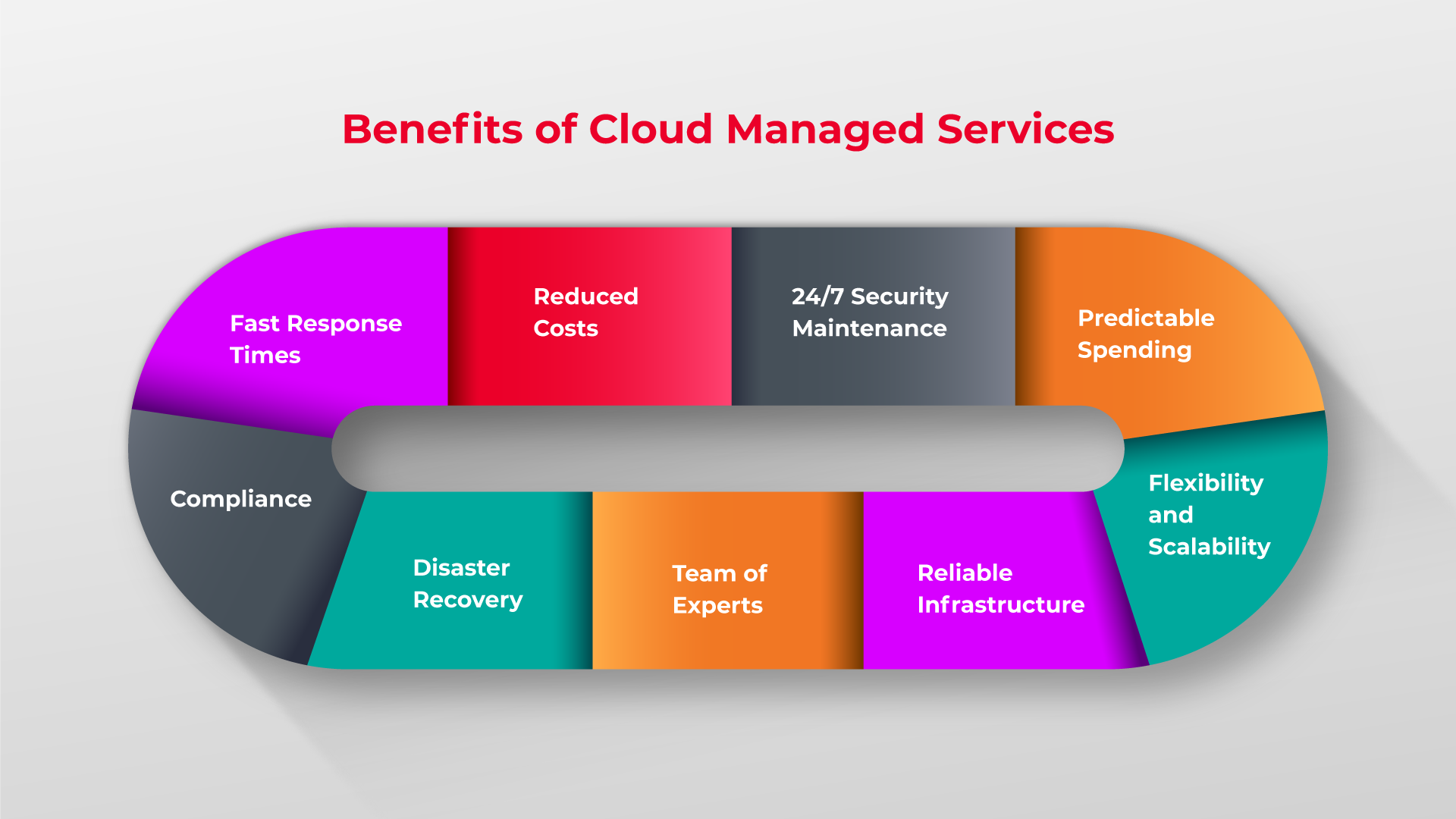
Benefits of Cloud Service Provisioning
In the realm of Cloud Service Provisioning, businesses reap the rewards of reduced costs by shifting from capital-intensive investments in hardware and software to pay-as-you-go models. This nimble approach enhances financial flexibility and operational efficiency.
Scalability emerges as a cornerstone benefit, enabling organizations to effortlessly adjust resources based on fluctuating needs. With cloud services, scaling up or down occurs swiftly, catering to dynamic business requirements with optimal resource utilization.
Agility takes center stage in the business landscape with Cloud Service Provisioning, empowering companies to adapt promptly to market dynamics. The agility offered by cloud services fosters innovation, accelerates time-to-market, and fosters strategic decision-making.
Security concerns find a robust solution in Cloud Service Provisioning, as providers prioritize stringent security protocols. With comprehensive security measures and compliance certifications, businesses can rest assured that their data is safeguarded against cyber threats, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.

Exploring the World of Cloud Service Provisioning Models
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS, a foundational cloud model, grants users access to essential computing components such as servers, storage, and networking. This model allows businesses to avoid the complexity of managing physical hardware and scale resources according to their needs, optimizing flexibility and cost-efficiency in cloud service provisioning.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS represents a comprehensive platform for app development and deployment, providing a ready environment with operating systems, middleware, and databases. By offering a complete setup, PaaS streamlines the development process, allowing businesses to focus on innovation rather than infrastructure management, thereby accelerating time to market for applications.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS revolutionizes software delivery by enabling users to access fully functional applications through the internet, eliminating the necessity for local installations. This model offers convenience, scalability, and automatic updates, ensuring seamless accessibility from any device, anywhere, at any time, making software deployment hassle-free and cost-effective.
FaaS (Function as a Service)
FaaS, a serverless computing model, empowers developers to execute code without the burden of infrastructure management. By abstracting the servers, FaaS allows for efficient execution of functions in response to specific events, optimizing resource utilization and enhancing agility in application development, leading to enhanced scalability and reduced operational complexities.

Key Considerations for Choosing a Cloud Service Provider
Reliability and Uptime
When selecting a cloud service provider, prioritizing reliability and uptime is paramount. Opt for a provider that guarantees high availability and optimal performance to ensure uninterrupted access to your services and data. Conduct thorough research on the provider’s track record in maintaining dependable service levels to avoid potential disruptions.
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are non-negotiable factors in choosing a cloud service provider. Evaluate the provider’s security protocols, data encryption methods, and compliance certifications. Ensuring alignment with industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001 is crucial for safeguarding your sensitive information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are key components to consider for future-proofing your cloud infrastructure. Opt for a provider capable of scaling resources on-demand to accommodate your evolving business needs. Choose a flexible service model that allows customization and adaptability to seamlessly align with your growth trajectory without operational bottlenecks.
Cost Structure
Understanding the cost structure of a cloud service provider is critical for effective budget management. Clarify the pricing model, including subscription fees, usage charges, and potential hidden costs. Ensure transparency in billing practices and choose a provider offering a cost-effective solution that aligns with your financial objectives and avoids unexpected financial strain.
Best Practices for Cloud Service Provisioning
Defining Clear Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Establishing detailed SLAs is paramount in cloud service provisioning to guarantee the quality of services provided by the cloud provider. SLAs outline performance metrics, uptime guarantees, and response times, critical for maintaining service levels and meeting business objectives effectively. Clear SLAs foster transparency, accountability, and trust between the service provider and the client, ensuring smooth operations and performance consistency.
Implementing Proper Access Controls and Security Measures
Security is a top priority in cloud service provisioning. Implement robust access controls, encryption protocols, and data protection mechanisms to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access or breaches. A multi-layered security approach, including identity management and regular security audits, is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data in the cloud environment.
Monitoring and Optimizing Cloud Usage
Efficient cloud resource management is key to cost optimization and performance enhancement. Regularly monitor resource utilization, analyze performance metrics, and identify opportunities for optimization. By streamlining resource allocation, resizing instances, and leveraging automation tools, organizations can optimize costs, improve scalability, and ensure optimal performance in their cloud environment.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Cloud Strategy
The dynamic nature of business demands continuous assessment and evolution of cloud strategies. Regularly review your cloud architecture, applications, and services to align with changing business requirements, technological advancements, and industry trends. By staying agile, proactive, and responsive to market shifts, organizations can enhance competitiveness, innovation, and operational efficiency through strategic cloud adoption and adaptation.