Welcome to the Ultimate Guide to Cloud Service Replication! In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of cloud service replication, a critical component in ensuring data protection and availability in the digital landscape. From exploring the various benefits and types of replication to uncovering best practices and real-world case studies, this guide is designed to equip IT professionals with the knowledge and insights needed to navigate the complexities of data replication in cloud environments.
Discover how leading cloud service providers leverage Cloud service replication to enhance data redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities. Join us as we examine the key considerations and strategies for implementing effective replication solutions in your organization’s cloud infrastructure.
Exploring the Essence of Cloud Service Replication
Cloud Service Replication plays a pivotal role in fortifying data availability and shielding against unforeseen data loss incidents. By duplicating data across various locations or devices, replication acts as a safety net, ensuring seamless data accessibility even in the face of hardware failures, natural calamities, or inadvertent human errors. The essence of replication lies in its ability to amplify data durability and resilience, forming a cornerstone in robust data protection strategies.
When it comes to devising replication strategies, organizations delve into the intricacies of recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs), tailoring replication mechanisms to meet specific business needs. These objectives are paramount in shaping the replication framework, dictating how swiftly data should be recovered and mitigating data loss risks. Balancing RTOs and RPOs is essential for crafting efficient data replication strategies that align with business continuity requirements and operational constraints.
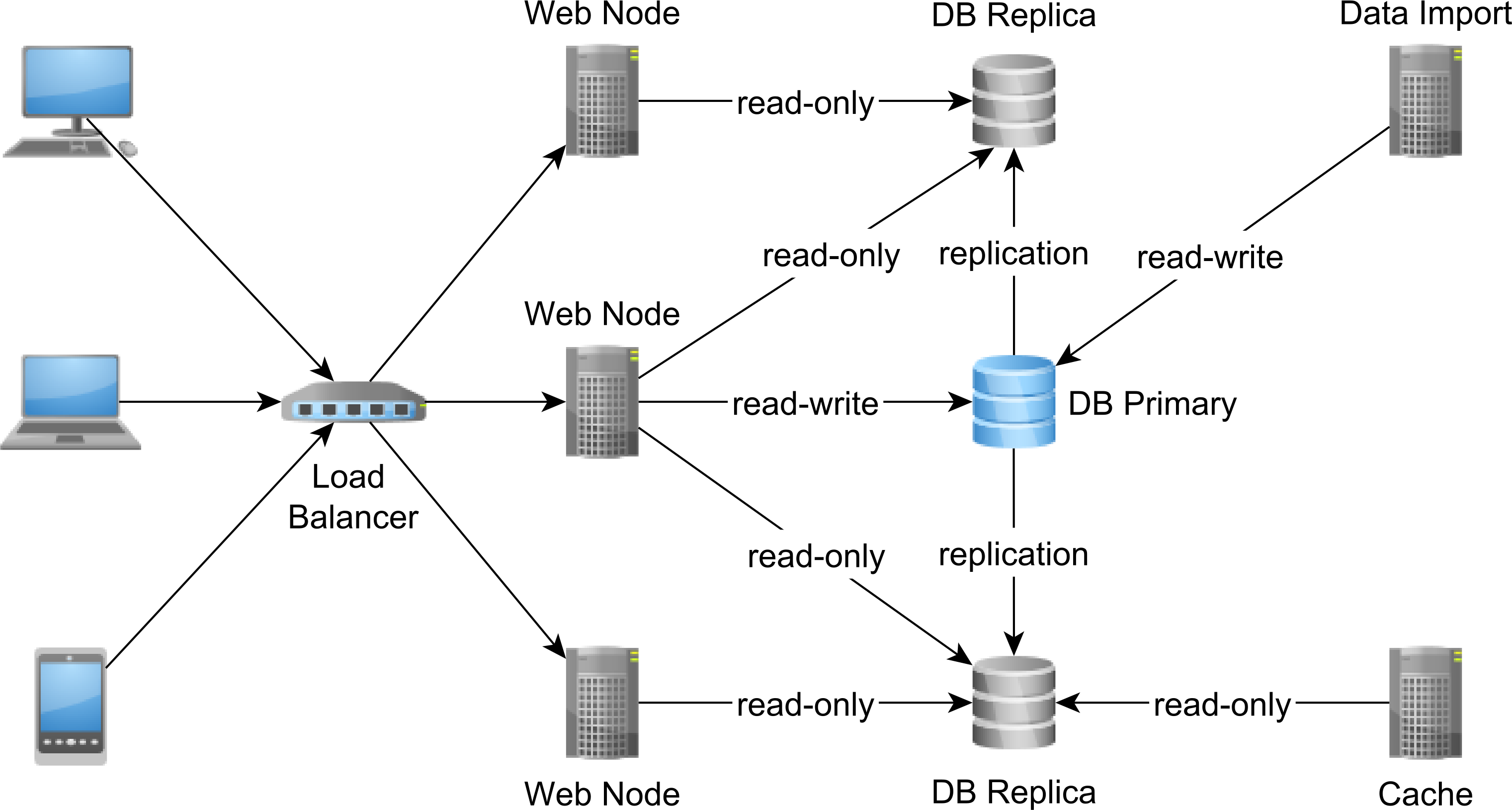
The landscape of cloud service replication boasts a diverse array of methods, each catering to distinct data replication needs. Synchronous replication ensures data is mirrored instantaneously, guaranteeing real-time consistency but potentially impacting performance. Asynchronous replication, on the other hand, introduces a slight delay in data duplication, offering flexibility in trade-offs between performance and consistency. Multi-site replication extends replication capabilities across geographically dispersed locations, bolstering disaster recovery readiness and geographical redundancy.
In essence, understanding the dynamics of cloud service replication unveils a world where data protection transcends mere backups, evolving into a sophisticated orchestration of redundancy, resilience, and risk mitigation strategies. By exploring the nuances of replication methods and aligning them with organizational objectives, IT professionals can sculpt robust data replication frameworks that stand as bastions of data integrity and availability in the ever-evolving digital realm.

Maximizing Data Protection with Cloud Service Replication
Improved Data Resilience and Risk Mitigation
Implementing cloud service replication significantly boosts data resilience by creating redundant copies of critical data. This redundancy minimizes the risk of data loss due to hardware failures, human errors, or cyberattacks. By having duplicate data stored across different locations, organizations ensure data availability and integrity, safeguarding against unforeseen data loss scenarios.
Enhanced Data Accessibility and Availability
Cloud service replication ensures uninterrupted data accessibility even during maintenance periods or outages. By replicating data across geographically dispersed servers, users can seamlessly access information without disruptions. This high availability feature enables businesses to maintain operational continuity, providing users with uninterrupted access to crucial data and applications.
Rapid Recovery in Disaster Scenarios
Cloud service replication plays a pivotal role in disaster recovery strategies by enabling swift data restoration. In the event of disasters or disruptions, replicated data allows for speedy recovery processes, minimizing downtime and operational impact. With real-time replication capabilities, organizations can quickly recover data and resume operations, ensuring business continuity and minimizing financial losses.
Compliance Adherence and Data Security
Adopting cloud service replication aids businesses in meeting data protection regulations and industry standards. Replication solutions often incorporate encryption and secure transmission protocols to maintain data integrity and confidentiality. By adhering to regulatory requirements through robust replication practices, organizations enhance data security, build trust with customers, and mitigate legal risks associated with data breaches.
Understanding the Types of Replication in Cloud Services
In the realm of cloud service replication, various strategies cater to different needs. Synchronous Replication ensures real-time data mirroring without loss, prioritizing data integrity at the potential expense of performance. On the flip side, Asynchronous Replication introduces a slight delay, yet boosts efficiency by decoupling data write operations.
Multi-Site Replication expands data protection horizons by duplicating information across diverse geographical regions. This approach serves as a robust safeguard against localized outages or disasters, enhancing overall data resilience.
In the scenario of Active-Passive Replication, a primary server actively manages operations while secondary servers remain on standby, ready to assume control seamlessly. This setup optimizes high availability, ensuring uninterrupted services in case of primary server failures.

Mastering Best Practices for Cloud Service Replication
Defining Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs)
Establishing clear RTOs and RPOs is crucial for effective cloud service replication. Define how quickly systems need to be restored (RTO) and how much data loss is acceptable (RPO) to tailor replication strategies accurately. This clarity ensures a streamlined approach to data protection and recovery.
Choosing the Right Replication Methodology
Selecting the ideal replication method demands a deep understanding of performance and recovery needs. Whether asynchronous, synchronous, snapshot-based, or continuous data protection, aligning the choice with specific requirements optimizes data availability and minimizes downtime effectively.
Implementing Automated Replication Processes
Automating replication workflows reduces the dependency on manual interventions, enhancing efficiency and reliability. By incorporating automation tools, cloud service replication can operate seamlessly, ensuring timely data synchronization and minimizing the risk of human errors impacting data integrity.
Regular Testing for Data Integrity and Recovery Assurance
Frequent testing of replication configurations is imperative to validate data integrity and recovery capabilities. Conducting simulation drills and failover tests helps identify vulnerabilities, fine-tune processes, and guarantee that in the event of a disaster, data can be recovered successfully.
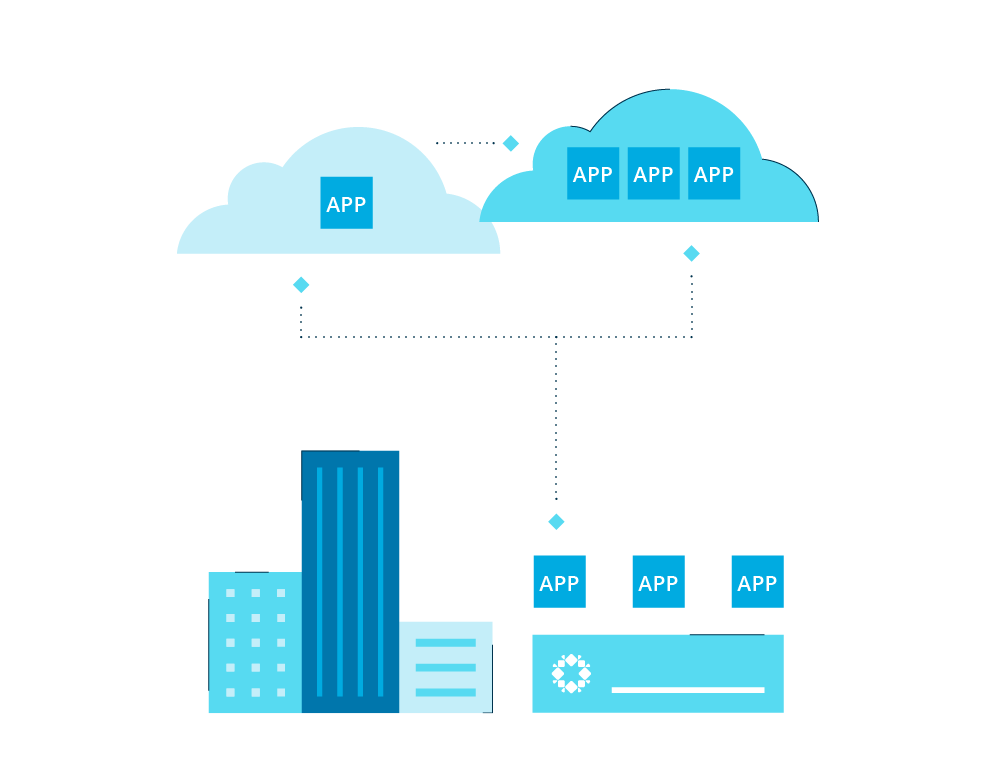
Key Considerations for Cloud Service Replication
Impact on Network Bandwidth and Storage Costs
When considering cloud service replication, it’s crucial to analyze how replication can affect network bandwidth and storage expenses. Replicating large volumes of data can strain network resources and lead to increased costs, making it vital to optimize replication processes to minimize these impacts.
Ensuring Data Consistency
Maintaining data consistency during replication demands meticulous planning and management. Discrepancies between original data and replicated data can lead to integrity issues, emphasizing the need for robust consistency mechanisms to ensure accurate replication and data integrity across systems.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Protecting replicated data from unauthorized access is paramount. Implementing stringent security protocols, encryption mechanisms, and access controls is essential to safeguard replicated data from potential breaches, ensuring confidentiality and integrity throughout the replication process.
Compliance Requirements
Navigating compliance regulations is critical in designing effective replication strategies. Organizations must align replication practices with industry-specific compliance requirements to meet data retention policies and regulatory standards. Adhering to these guidelines ensures data protection and legal compliance, mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
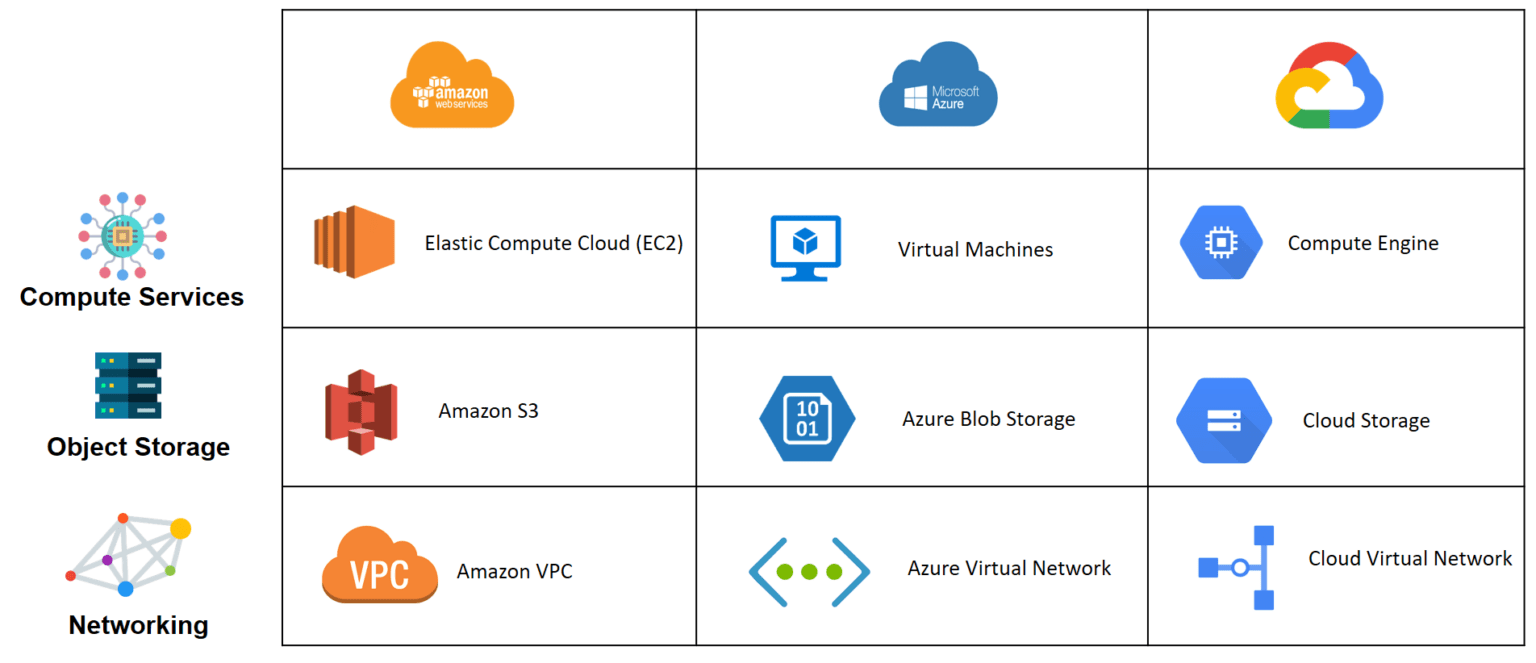
Leading Cloud Service Providers with Replication Features
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands out with its robust replication offerings, including Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) replication ensuring durable block-level storage replication. Additionally, AWS provides Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) replication, enabling high availability and failover capabilities for database instances vital for disaster recovery strategies.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure shines in the realm of replication services by offering Azure Site Recovery, facilitating seamless disaster recovery planning for virtual machines and physical servers. Furthermore, Azure Storage replication enhances data redundancy and availability across Azure regions, enhancing data protection and continuity in cloud environments.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) excels in replication solutions through its Google Cloud Storage multi-region buckets, ensuring data redundancy and resilience across multiple geographic locations. Moreover, GCP’s Cloud SQL replication empowers users to create redundant copies of their databases, bolstering data integrity and disaster recovery preparedness.
IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud enriches its replication capabilities with IBM Cloud Databases for PostgreSQL, enabling users to easily replicate data for high availability and fault tolerance, essential for critical data-driven applications. Additionally, IBM Cloud Databases for MongoDB provides robust replication features, ensuring data consistency and durability in distributed environments.
In the competitive landscape of cloud computing, these leading providers offer a spectrum of replication features vital for IT professionals in establishing comprehensive data protection strategies and maintaining uninterrupted service operations. Leveraging these diverse replication options, cloud service administrators can enhance their disaster recovery preparedness and data redundancy, ensuring business continuity in the face of unexpected disruptions.

Successful Cloud Service Replication: Real-World Case Studies
Example 1: Company X Revolutionizes Data Recovery
Company X’s adoption of synchronous replication technology led to a significant reduction in data recovery time, from days to mere hours. By synchronizing data in real-time across multiple locations, they ensured minimal downtime and enhanced data availability, showcasing the power of proactive disaster recovery strategies.
Example 2: Resilience in Action at Company Y
During a natural disaster, Company Y’s multi-site replication setup played a pivotal role in maintaining uninterrupted business operations. By dispersing data across geographically diverse locations, they safeguarded against localized disruptions, highlighting the importance of redundancy and geographical diversity in ensuring continuous service delivery.
Example 3: Company Z Navigates Compliance Challenges
Company Z successfully aligned with industry regulations by implementing automated replication processes. This proactive approach not only ensured data consistency and integrity but also demonstrated a commitment to compliance requirements. Automated replication not only eased operational burdens but also provided a robust framework for meeting regulatory obligations, showcasing the intersection of data protection and legal compliance in cloud environments.