Cloud service availability is a critical aspect in today’s digital landscape, impacting businesses’ operations and user experience. Understanding the factors influencing cloud service availability, such as network latency, data center location, and infrastructure redundancy, is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted service delivery. Monitoring and measuring techniques play a vital role in assessing availability levels, identifying potential downtime risks, and implementing proactive strategies to enhance performance. Furthermore, selecting high availability cloud providers is key to maintaining seamless services and mitigating disruptions, making it essential for businesses to strategize their cloud architecture effectively.
Key Factors Influencing Cloud Service Availability
Infrastructure Reliability
Ensuring robust infrastructure reliability is foundational for high cloud service availability. From hardware resilience to network stability and data center redundancy, each component plays a pivotal role in maintaining uninterrupted service delivery. By implementing redundant systems and failover mechanisms, cloud providers can enhance reliability and minimize downtime risks, ultimately optimizing cloud service availability.
Software Updates Impact
The regular maintenance, patches, and upgrades of cloud software are critical factors affecting availability. Timely updates not only enhance performance and security but also mitigate potential service disruptions. Careful planning and testing of software updates are essential to ensure seamless transitions and minimize the impact on availability, safeguarding against unexpected downtimes that could affect users’ experience.
Security Breaches and Disruptions
Cybersecurity threats pose a significant risk to cloud service availability. Security breaches, ranging from DDoS attacks to data breaches, can lead to service interruptions, compromising data integrity and availability. Implementing robust security measures, such as encryption protocols and multi-factor authentication, is vital in safeguarding against unauthorized access and ensuring continuous service availability.
Natural Disasters and Outages
Unforeseen events like natural disasters, power outages, or network failures can critically impact cloud infrastructure and availability. Cloud providers must have disaster recovery plans in place, including data backups, geographically distributed data centers, and redundant power supplies, to mitigate the effects of such events and uphold service availability during challenging circumstances.
Incorporating redundant systems, prioritizing software updates, strengthening cybersecurity defenses, and preparing for unexpected disruptions are essential aspects to consider when aiming to optimize cloud service availability. By proactively addressing these key factors, businesses can fortify their cloud infrastructure and ensure consistent and reliable service delivery to their users.

Measuring and Monitoring Availability
Service level agreements (SLAs) play a pivotal role in defining Cloud Service Availability targets between providers and users, outlining uptime guarantees and potential penalties for breaches. These agreements set clear expectations and accountability, ensuring a reliable service experience for businesses. Monitoring tools are essential for tracking uptime, downtime, and response times, enabling real-time visibility into service performance and adherence to SLA parameters.
Metrics like mean time to recovery (MTTR) and mean time between failures (MTBF) are critical in quantifying the reliability and robustness of cloud services. MTTR measures the average time taken to restore services after an incident, while MTBF calculates the average time elapsed between two consecutive service failures. These metrics provide valuable insights into overall system availability and help in identifying areas for improvement.
Proactive monitoring strategies are imperative for identifying potential issues before they escalate into downtime incidents. By continuously monitoring key performance indicators, anomalies can be detected early, allowing for prompt intervention and proactive maintenance to prevent service disruptions. This proactive approach enhances the overall Cloud Service Availability by minimizing risks and ensuring continuous service delivery to users.
Strategies for Enhancing Cloud Service Availability
Redundancy and Failover Mechanisms
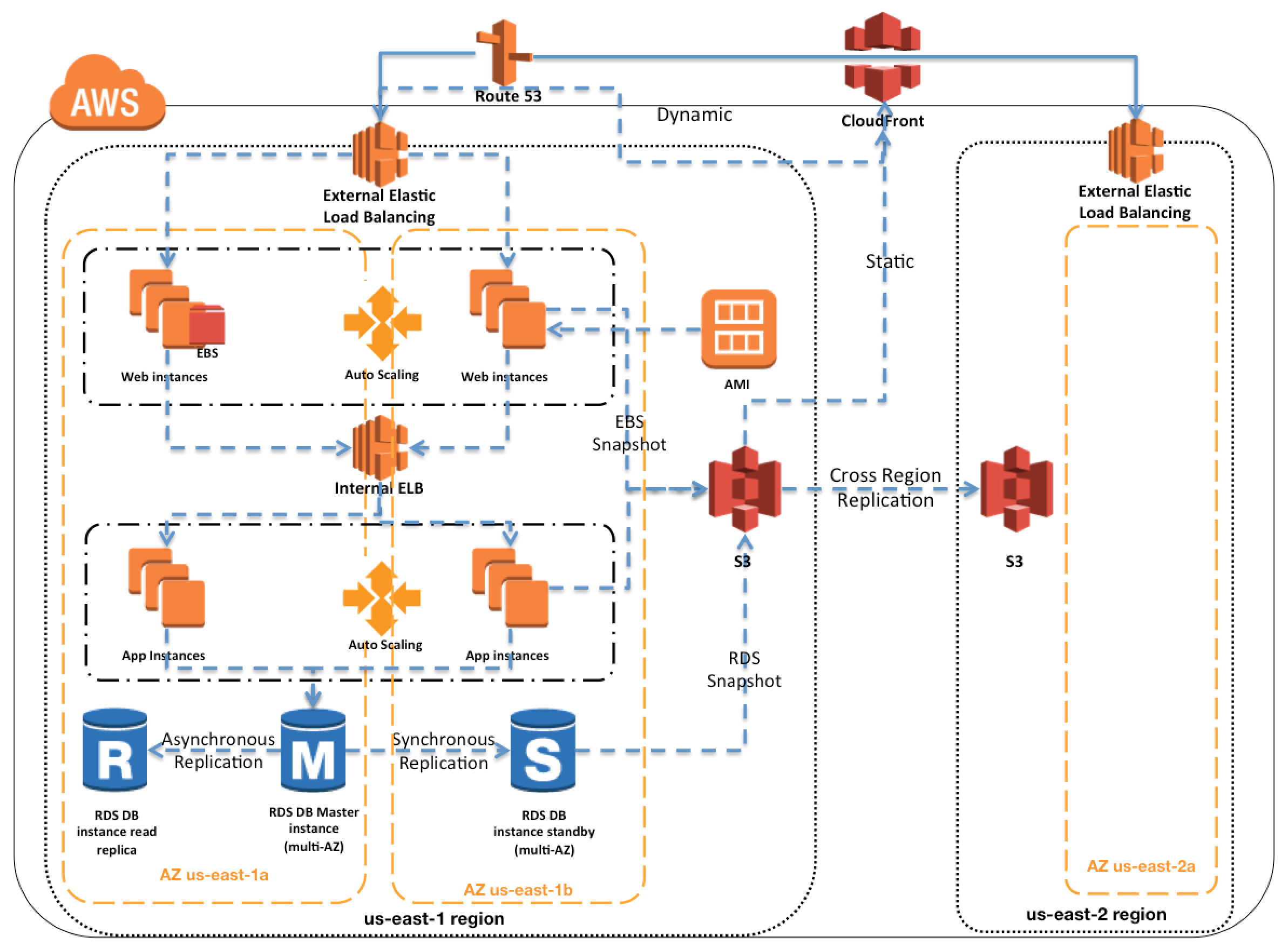
Implementing redundancy through multiple servers and data centers is paramount for ensuring uninterrupted service delivery. Failover mechanisms play a crucial role in seamlessly transitioning operations in case of hardware failures or network disruptions, thereby maintaining high Cloud Service Availability.
Automated Recovery Systems
Utilizing automated recovery systems enables swift responses to outages and data loss incidents. Automation streamlines the recovery process, reducing downtime and enhancing the overall reliability of cloud services, ultimately boosting Cloud Service Availability for businesses.
Regular Maintenance and Updates
Proactive measures like regular maintenance and timely software updates are essential for optimizing cloud infrastructure. By staying ahead of potential issues through continuous monitoring and upkeep, organizations can prevent service disruptions and maintain high levels of Cloud Service Availability.
Disaster Recovery Plans
Developing robust disaster recovery plans is critical to mitigating the impact of natural disasters or unforeseen events. By strategizing and testing disaster recovery scenarios, businesses can minimize downtime, swiftly recover data, and uphold continuous service availability to meet customer demands.

Benefits of High Cloud Service Availability
Enhanced User Experience
High cloud service availability translates to minimal downtime, ensuring users have uninterrupted access to services, boosting satisfaction and productivity. Seamless service delivery fosters trust and reliability, enhancing the overall user experience.
Increased Productivity
Business operations thrive with uninterrupted cloud services. High availability fosters seamless collaboration, file sharing, and real-time communication, empowering teams to work efficiently without disruptions, ultimately increasing productivity and driving business success.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Reliable cloud services are the cornerstone of happy customers. Consistent availability and performance create trust, loyalty, and satisfaction among users, leading to positive relationships and potential referrals, ultimately benefiting the business’s reputation and growth.
Competitive Advantage
High cloud service availability sets providers apart in a competitive market. Reliability, fast response times, and minimal downtime attract businesses seeking dependable services. Being known for high availability can be a key selling point, driving customer acquisition and retention, thus gaining a competitive edge in the industry.

Best Practices for Cloud Service Availability
Implement Multi-Region and Multi-Cloud Strategies
To enhance Cloud Service Availability, deploying applications across multiple regions or cloud providers diversifies risks and reduces downtime. This strategy mitigates the impact of localized outages and ensures redundancy for uninterrupted service delivery, fostering a resilient architecture for businesses.
Utilize Auto-Scaling and Load Balancing
Auto-scaling and load balancing mechanisms dynamically adjust resource allocation based on traffic fluctuations, optimizing performance during peak loads. By efficiently distributing workloads and resources, businesses can maintain consistent service availability and responsiveness, catering to fluctuating user demands effectively.
Regular Performance and Security Audits
Conducting routine performance and security audits is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities, optimizing system efficiency, and enhancing Cloud Service Availability. By proactively addressing issues through audits, businesses can mitigate risks, maintain operational excellence, and uphold a robust security posture in the cloud environment.
Train Staff on Cloud Availability Best Practices
Educating staff on cloud availability best practices equips them with the knowledge and skills to respond effectively to availability challenges. Training sessions on incident response, disaster recovery protocols, and cloud architecture principles empower teams to contribute proactively to maintaining high availability standards, fostering a culture of operational readiness and resilience.