Cloud service data privacy is a critical aspect of safeguarding sensitive information in today’s digital landscape. With the increasing reliance on cloud technology, understanding key regulations such as GDPR and CCPA is essential to ensure compliance and data protection. In addition to regulatory requirements, implementing robust encryption measures and access controls is imperative to mitigate risks and maintain the confidentiality of your data. Stay informed about cloud service data privacy to safeguard your valuable information effectively.

Exploring Cloud Service Data Privacy
Cloud service data privacy is the cornerstone of safeguarding sensitive information stored and processed by cloud service providers. This encompasses a comprehensive set of practices, such as adhering to data protection regulations, implementing encryption protocols, stringent access controls, and robust security monitoring. Understanding these multifaceted measures is paramount for organizations contemplating the integration of cloud services into their operations. Cloud service data privacy dictates the level of trust and security organizations can place in cloud technologies.

Key Data Privacy Regulations
Understanding GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a pivotal regulation in the EU, setting stringent guidelines on personal data handling. Complying with GDPR is crucial for businesses to protect individuals’ privacy rights effectively. On the other hand, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) focuses on safeguarding Californian residents’ personal information rights, emphasizing transparency and accountability. In the healthcare sector, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) governs the secure handling of protected health information in the U.S., aiming to ensure data security and confidentiality in healthcare settings.
GDPR Compliance and Its Impact on Cloud Services
Businesses operating within the EU or dealing with EU citizens’ data must adhere to GDPR mandates, including data minimization, lawful processing, and individual data rights. When leveraging cloud services, organizations must ensure their cloud providers comply with GDPR to safeguard data privacy. Understanding GDPR’s nuances aids businesses in implementing robust data protection measures and fostering trust with their customers regarding cloud service data privacy.
CCPA’s Influence on Cloud Service Data Privacy
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) grants Californian consumers control over their personal information, compelling businesses to disclose data practices and provide opt-out options. Cloud service providers processing Californian residents’ data must align their practices with CCPA’s requirements to uphold data privacy. By integrating CCPA compliance measures, organizations can enhance transparency and accountability in their cloud data management, thus strengthening privacy protections for individuals.
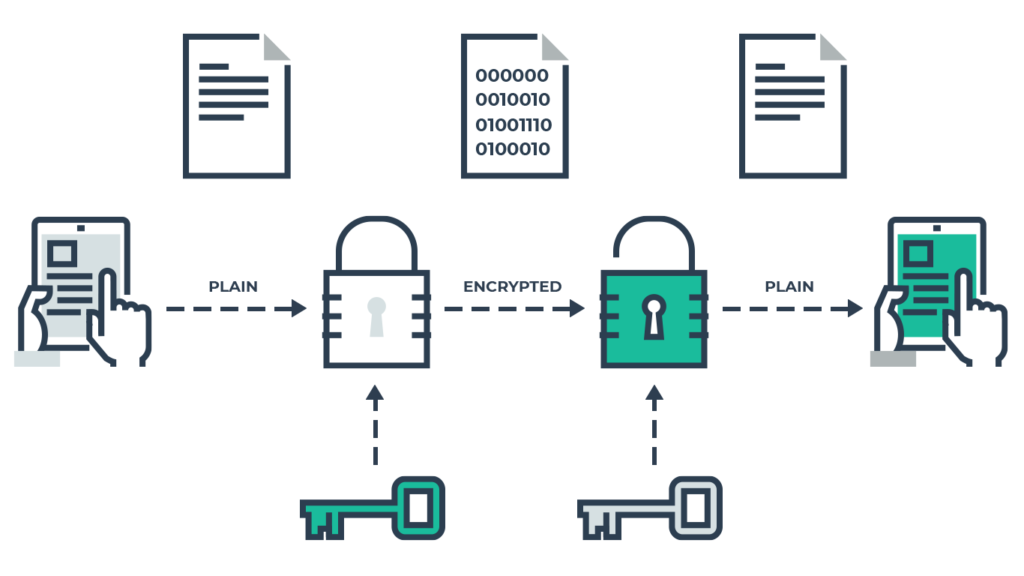
Advanced Encryption Techniques for Enhanced Data Protection
Encryption for Data Security
Encryption serves as a foundational shield for cloud service data privacy, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure during storage and transmission. By encoding data, unauthorized individuals are unable to decipher its contents, bolstering confidentiality.
Provider-Driven Encryption Solutions
When opting for cloud services, providers often furnish advanced encryption mechanisms like AES-256 to fortify data protection. This robust encryption standard enhances the security posture by making data indecipherable without the requisite decryption keys.
Additional Data Protection Strategies
Complementing encryption, tactics like tokenization and anonymization can further enhance data security in cloud environments. Tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique tokens, while anonymization conceals identifying information, reducing vulnerability to breaches.
Enrich your understanding of cloud service data privacy by embracing intricate encryption methodologies to fortify data protection mechanisms effectively. By leveraging cutting-edge encryption protocols and supplementary data protection technologies, organizations can safeguard their critical information assets comprehensively.
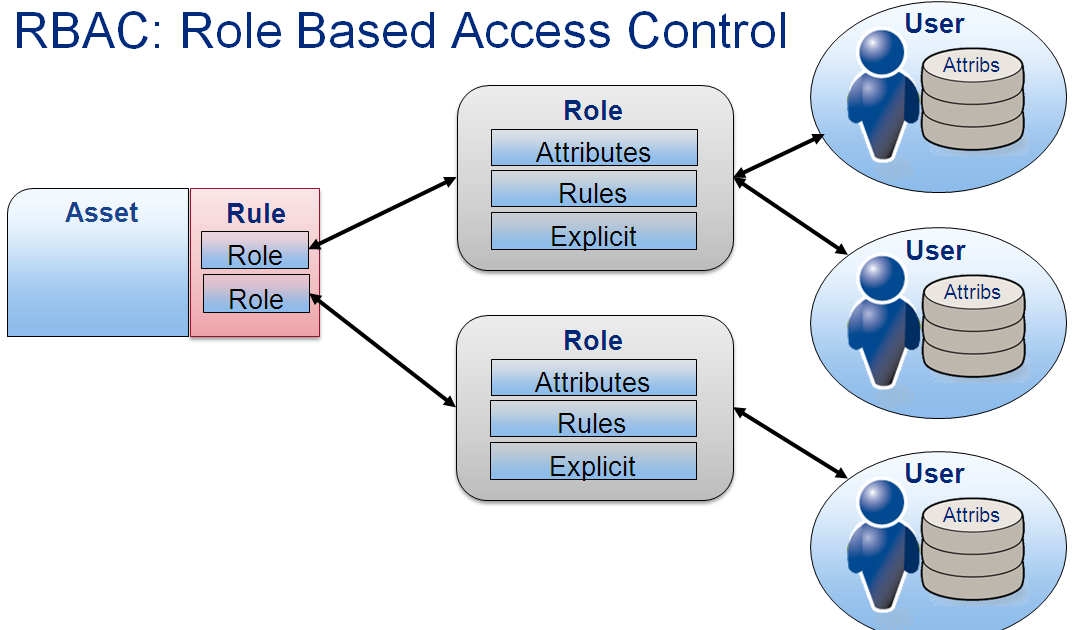
Enhancing Data Security Through Access Controls and Authorization
Access Controls: Safeguarding Data Privacy
Access controls play a pivotal role in upholding cloud service data privacy by specifying user permissions and functionalities within the system. They regulate user access levels, dictating who can view, modify, or delete sensitive information, thus minimizing unauthorized data exposure.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
Implementing RBAC and ABAC strategies enable organizations to streamline access management effectively. RBAC assigns permissions based on job roles, simplifying administration. ABAC, on the other hand, considers specific attributes for access, enhancing granularity in authorization processes for refined data protection.
Strengthening Security with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA acts as a robust barrier against unauthorized access attempts by requiring users to provide multiple credentials, such as passwords, biometrics, or OTPs. This extra layer of verification bolsters data security, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information, thereby fortifying cloud service data privacy.

Enhancing Cloud Service Data Privacy through Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Security Monitoring for Threat Detection
Security monitoring is vital in maintaining cloud service data privacy. By monitoring system activity continuously, potential threats can be detected early. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) tools are instrumental in this process, providing real-time insights to safeguard sensitive information.
Incident Response Plans for Effective Resolution
Incident response plans are essential components of cloud data privacy measures. These plans outline predefined procedures to follow in the event of a data breach or security incident. Prompt and efficient responses to incidents help minimize the impact on data integrity and confidentiality, ensuring a proactive approach to data protection.
By integrating robust security monitoring practices and well-defined incident response strategies, organizations can strengthen their cloud service data privacy framework, enhancing their ability to detect and respond effectively to potential threats and incidents, ultimately safeguarding their valuable information assets.

Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model for Data Privacy
In the realm of cloud computing, ensuring cloud service data privacy involves a collaborative effort shared between the cloud service provider and the customer. The provider shoulders the responsibility of safeguarding the infrastructure and platform where the data resides. Conversely, the customer plays a pivotal role in securing their data and applications utilized within the cloud environment. This collaborative model ensures a comprehensive approach to data privacy protection.