Understanding Cloud Service Data Replication is crucial for businesses in today’s digital age. This process involves duplicating data to ensure its availability and reliability in case of system failures or disasters. By implementing cloud service data replication, organizations can enhance data access, improve disaster recovery capabilities, and ensure data integrity. This article will delve into the benefits, types, implementation strategies, and best practices of Cloud service data replication to help you navigate the complexities of data management in the cloud.
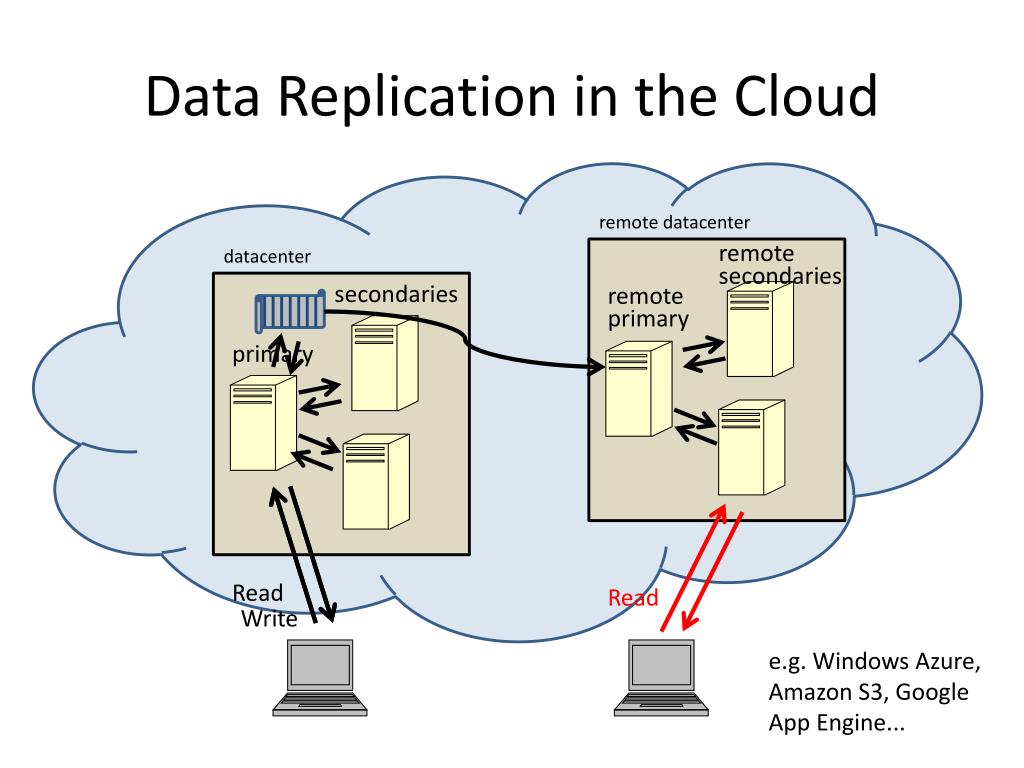
Cloud service data replication plays a pivotal role in ensuring data consistency and availability across distributed cloud environments. Organizations can leverage various replication types such as synchronous, asynchronous, and snapshot replication to meet their specific data protection and recovery requirements. Understanding the nuances of each replication type is essential for implementing a robust data replication strategy that aligns with business objectives. In this article, we will explore the nuances of Cloud service data replication, shedding light on its benefits and providing insights into effective implementation practices for optimized data management in the cloud.

Delving into the Essence of Cloud Service Data Replication
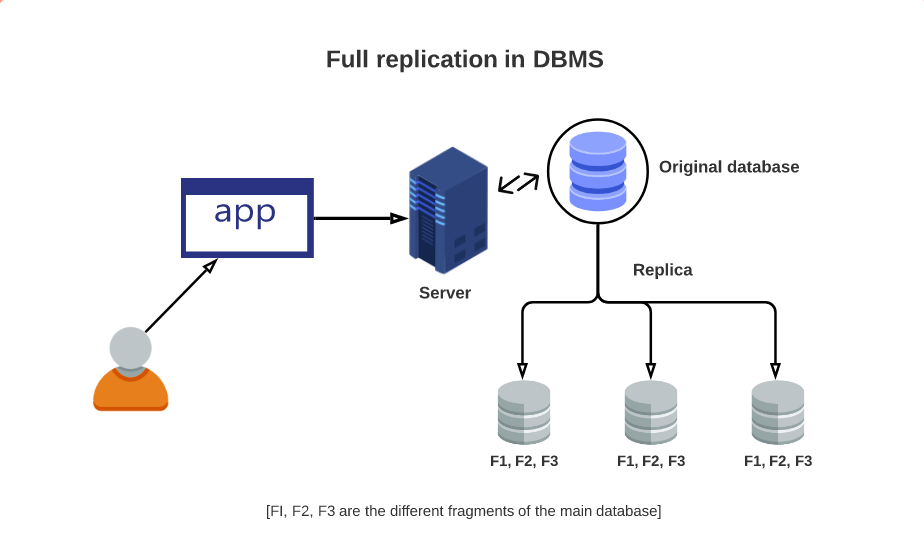
Cloud Service Data Replication stands as a pillar of cloud computing, offering paramount benefits like data availability, redundancy, and disaster recovery readiness. This process revolves around duplicating data sets from one site to another, crafting replicas that bolster data protection and fortify resilience against potential disruptions. The techniques employed in data replication vary, adapting to specific needs like data integrity demands, recovery speed targets, and financial constraints. At its core, Cloud Service Data Replication embodies the essence of safeguarding invaluable digital assets in the face of unforeseen challenges, ensuring continuity and reliability in a dynamic cloud landscape.
Benefits of Cloud Service Data Replication
Cloud Service Data Replication offers a multitude of benefits to organizations seeking to fortify their data management strategies. One prominent advantage is the enhanced data availability and accessibility it provides. By duplicating data across multiple servers or data centers, organizations can significantly reduce downtime risks and ensure quick access to critical information, bolstering operational continuity in the face of unforeseen disruptions.
Another key benefit of Cloud Service Data Replication is the improved data protection it offers. In the event of hardware failures, natural disasters, or human errors, having replicated data safeguards against potential data loss, providing a safety net for crucial business information. This added layer of protection is vital for maintaining data integrity and business continuity, instilling confidence in data security measures.
Cloud Service Data Replication also excels in facilitating robust disaster recovery strategies. By creating backup copies of data in geographically diverse locations, organizations can ensure that their data remains secure and accessible even in the wake of catastrophic events. This redundancy not only streamlines recovery processes but also minimizes the impact of data loss, reinforcing overall resilience against unforeseen calamities.
Furthermore, data replication supports data locality, a crucial aspect for organizations with geographically dispersed users. By distributing replicated data closer to end-users, latency is reduced, enhancing performance and user experience. This strategic data distribution ensures that data access remains swift and seamless, catering to the dynamic needs of modern businesses operating across various geographical locations.
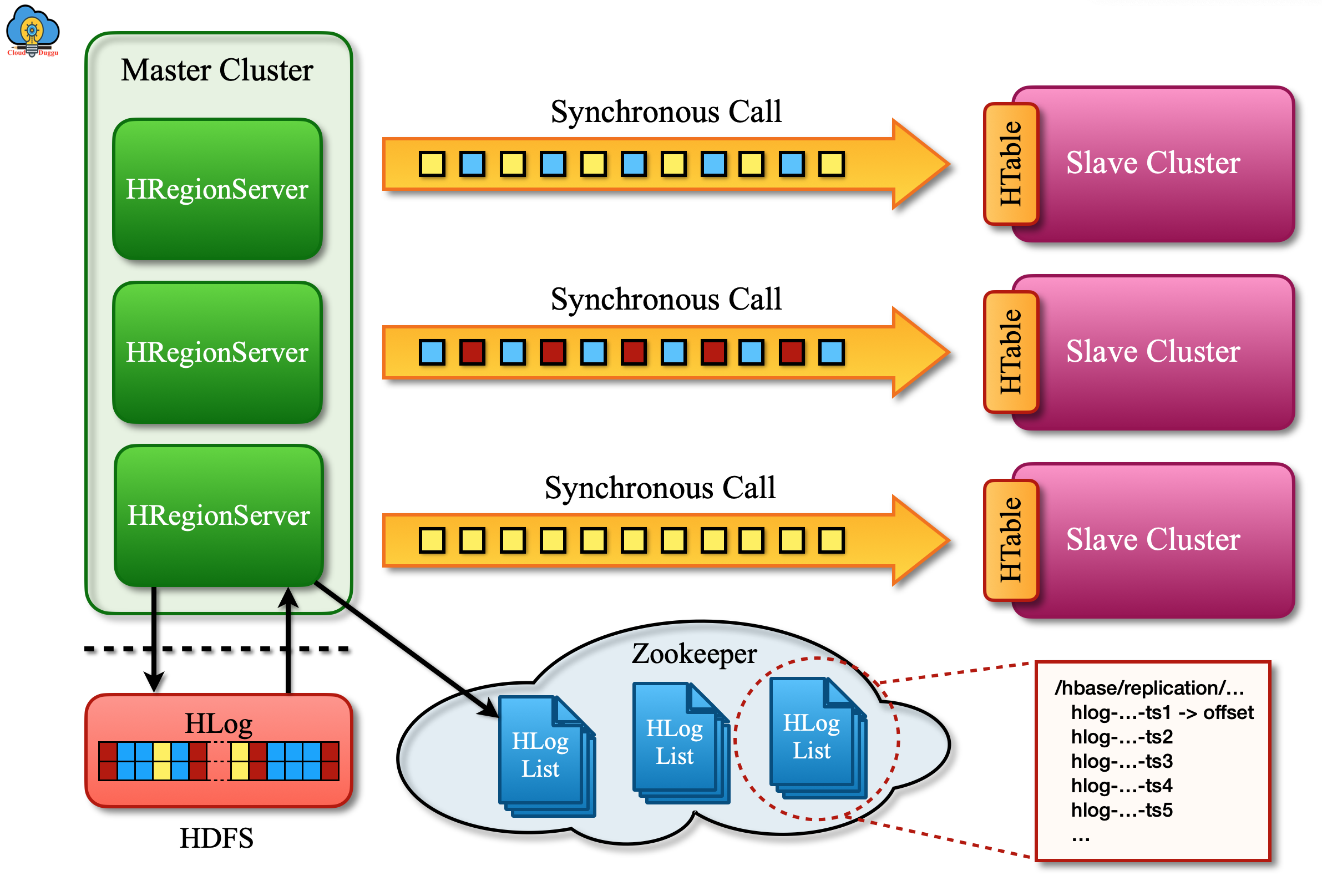
Types of Cloud Service Data Replication
In the realm of cloud service data replication, understanding the various types is crucial for designing a robust data protection strategy. Synchronous replication ensures real-time data consistency by instantly reflecting changes across all copies, ideal for critical systems demanding immediate updates and high data accuracy. This type guarantees minimal data loss in case of failures, emphasizing data integrity above all else.
Asynchronous replication involves copying data periodically, allowing for potential data loss during failures. While offering more flexibility in replication timing, this type may result in discrepancies between copies. Organizations with less stringent data consistency requirements can benefit from this approach, balancing performance and protection based on recovery point objectives.
Active-passive replication designates one primary server for write operations, while a secondary server remains passive until needed. This model focuses on failover scenarios, enabling rapid recovery by swiftly activating the secondary server when the primary one fails. It’s suitable for applications where rapid failover is critical, ensuring minimal downtime and continuity of services.
Employing active-active replication involves multiple servers actively handling write operations simultaneously. This approach offers enhanced availability, load balancing, and scalability by distributing data processing across multiple nodes. Companies seeking high availability and performance optimization often opt for active-active replication to leverage resources efficiently and improve fault tolerance.

Key Considerations in Choosing the Right Replication Strategy
Data Consistency & Recovery Time Objectives
When selecting a replication strategy for Cloud Service Data Replication, businesses should first assess their data consistency needs and recovery time objectives. Understanding how quickly data must be restored and the level of consistency required post-recovery is essential for choosing the right replication method.
Cost Implications & Cloud Service Options
Evaluate the cost implications of different replication strategies against available cloud service offerings. Consider factors such as bandwidth usage, storage costs, and any additional fees associated with the chosen replication approach. Assessing budget constraints and aligning them with available cloud service options is crucial for cost-effective data replication.
Replication Frequency & Data Retention Period
Determine how frequently data needs to be replicated and the retention period for replicated data. Factors such as data volatility, compliance requirements, and business continuity plans influence the replication frequency and data retention policies. Setting clear guidelines on replication intervals and data retention duration ensures efficient data management.
Security & Compliance Requirements
Security and compliance play a vital role in selecting a replication strategy. Evaluate the security measures offered by cloud service providers, encryption protocols, and compliance certifications relevant to your industry. Ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance with regulatory standards is paramount when choosing a replication strategy for Cloud Service Data Replication.

Implementing Cloud Service Data Replication
Implementing Cloud Service Data Replication: A Comprehensive Approach
Implementing Cloud Service Data Replication involves leveraging the cloud service provider’s native replication features for seamless data duplication. Additionally, organizations can opt for third-party tools to enhance replication capabilities, ensuring robust data redundancy. Configuring replication settings meticulously and monitoring replication status proactively are essential steps in maintaining data consistency and availability.
Leveraging Replication Tools and Services for Enhanced Data Protection
By harnessing third-party data replication tools and services, businesses can tailor replication strategies to meet specific requirements. These tools offer advanced features for efficient replication management, enabling organizations to customize replication schedules and prioritize critical data sets. This approach empowers businesses to achieve optimal data protection while streamlining data replication processes.
Ensuring Data Integrity through Rigorous Replication Testing
Testing the replication process is paramount to verify data integrity and validate recovery capabilities. By conducting routine tests, organizations can identify and address potential issues proactively, ensuring that data replication functions effectively in the event of system failures or disasters. Comprehensive testing guarantees the reliability of the replication process, safeguarding critical data assets effectively.
In summary, an effective implementation of Cloud Service Data Replication involves utilizing the cloud provider’s features, exploring third-party tools, configuring settings diligently, and conducting rigorous testing. This comprehensive approach ensures data redundancy, integrity, and availability, allowing organizations to fortify their data management strategies and bolster disaster recovery capabilities.
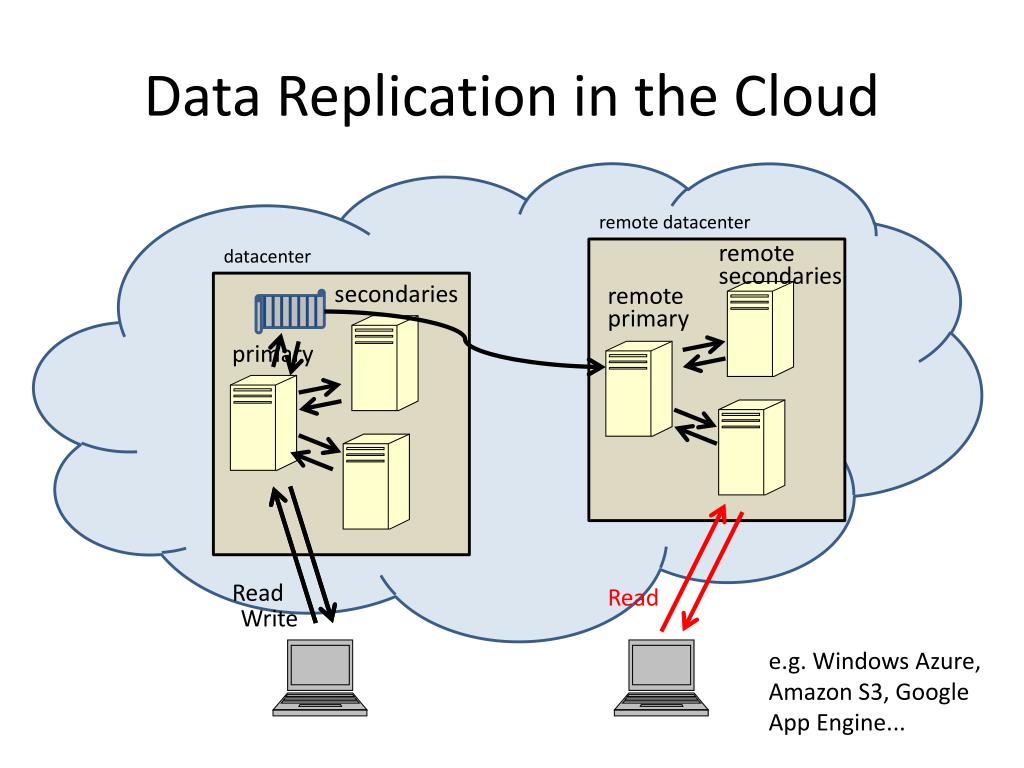
Best Practices for Cloud Service Data Replication
Regular Monitoring for Data Consistency
Regularly monitoring replication status and data consistency is vital to ensuring the integrity and accuracy of replicated data. By actively monitoring replication processes, IT professionals can promptly identify any issues or discrepancies, allowing for timely intervention and maintenance to prevent data loss or corruption. This practice minimizes the risk of data inconsistencies and optimizes the reliability of the replication system.
Automated Failover Mechanisms for Data Recovery
Implementing automated failover mechanisms is essential for seamless data recovery in the event of system failures or disruptions. By automating failover processes, organizations can swiftly switch to alternative replicated data sources, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous data availability. This proactive approach enhances data resilience and reinforces business continuity in critical situations.
Clear Data Retention and Deletion Policies
Establishing clear data retention and deletion policies is crucial for effective data management and compliance with regulations. By defining specific guidelines for retaining and deleting replicated data, organizations can optimize storage resources, streamline data access, and mitigate data privacy risks. Transparent policies ensure data governance and support regulatory requirements for data handling and protection.
Encryption for Data Security and Compliance
Encrypting replicated data adds an extra layer of security to safeguard sensitive information during transmission and storage. By employing encryption mechanisms, organizations can protect replicated data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations. Implementing robust encryption practices enhances data confidentiality, integrity, and compliance with data protection regulations, bolstering overall data security measures.

Use Cases for Cloud Service Data Replication
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning
Cloud service data replication is paramount for disaster recovery, ensuring uninterrupted operations during crises. By replicating data across geographically dispersed locations, businesses can swiftly recover from system failures or disasters, minimizing downtime and maintaining business continuity. This use case highlights the critical role of data redundancy in safeguarding against unforeseen disruptions.
Data Backup and Archival for Long-Term Data Preservation
Cloud service data replication facilitates robust data backup and archival practices, enabling organizations to store data securely for extended periods. This use case emphasizes the significance of replicating critical data to prevent loss and ensure long-term preservation. By leveraging replication technologies, businesses can safeguard against data corruption and mitigate risks associated with data loss.
Data Distribution for Improved Performance and Scalability
Cloud service data replication optimizes data distribution across multiple servers, enhancing performance and scalability. Organizations can efficiently manage data loads and access data more rapidly, improving overall system performance. This use case underscores the role of data replication in distributing workloads effectively, enhancing operational efficiency, and scaling resources to meet evolving business demands.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements for Data Protection and Retention
Cloud service data replication aids organizations in complying with stringent regulatory requirements for data protection and retention. By replicating data to secure locations, businesses can ensure data integrity, meet legal obligations, and mitigate risks of non-compliance. This use case stresses the importance of implementing robust data replication strategies to uphold data security standards and adhere to industry regulations.