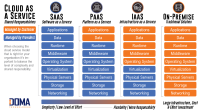
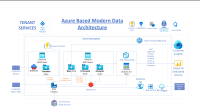
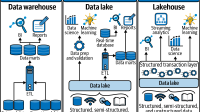
In today’s dynamic digital landscape, understanding cloud service fault tolerance is imperative for businesses seeking uninterrupted operations. This article delves into the significance of fault tolerance in cloud services, shedding light on its benefits, common techniques, implementation strategies, and best practices. Real-world case studies provide practical insights into how organizations can leverage fault tolerance in cloud environments to ensure resilience and reliability. Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or a curious learner, exploring the realm of cloud service fault tolerance is a crucial step towards fortifying your digital infrastructure.
Benefits of Fault Tolerance in Cloud Services
Enhancing Operational Continuity
Cloud Service Fault Tolerance significantly improves service uptime, minimizing downtime, and boosting user satisfaction. By proactively addressing potential failures, businesses can ensure uninterrupted access to services, enhancing operational continuity even in the face of unforeseen disruptions. This continuous availability plays a pivotal role in maintaining customer trust and loyalty.
Boosting Reliability and Resilience
Implementing fault tolerance in cloud services enhances overall reliability and resilience. Critical applications can continue functioning seamlessly despite hardware failures or network issues. This ensures that essential business operations remain unaffected, mitigating the risks associated with service interruptions. The ability to gracefully handle failures reinforces the platform’s dependability and trustworthiness.
Safeguarding Against Data Loss
One of the key benefits of fault tolerance in cloud services is the mitigation of data loss risks. By redundantly storing and safeguarding data, organizations can protect valuable information from accidental deletions, system malfunctions, or other unforeseen events. This proactive approach helps ensure data integrity and availability, minimizing the impact of potential disruptions on business operations.
Implementing Fault Tolerance in Cloud Architectures
In the realm of cloud service fault tolerance, a fundamental principle is to “Design for failure.” This entails anticipating failures and integrating fault tolerance mechanisms proactively during the architecture design phase. By assuming that failures are inevitable, businesses can build resilient cloud systems that can withstand unexpected disruptions, ensuring continuity of operations even under adverse circumstances.
When implementing fault tolerance in cloud architectures, selecting cloud services and infrastructure that come equipped with fault-tolerant technologies is paramount. Opting for platforms that inherently incorporate redundancy, failover mechanisms, and auto-recovery features can significantly enhance the overall fault tolerance of the system. This strategic choice can mitigate the impact of potential failures and enhance the reliability of cloud services.
Furthermore, a critical aspect of fault tolerance implementation is establishing robust monitoring and alerting systems. By deploying monitoring tools that continuously track system performance metrics and set up proactive alerts for potential issues, organizations can swiftly identify anomalies and respond promptly to impending failures. This proactive approach enables teams to address vulnerabilities before they escalate, minimizing downtime and service disruptions effectively.
By strategically embracing fault tolerance through designing for failure, leveraging fault-tolerant technologies in cloud services, and implementing robust monitoring and alerting mechanisms, businesses can fortify their cloud architectures against unforeseen disruptions. These proactive measures not only enhance system resilience but also contribute to ensuring uninterrupted service delivery and bolstering overall operational efficiency in cloud environments.

Cloud Service Providers and Fault Tolerance
Leveraging Fault-Tolerant Services
Major cloud providers offer robust fault-tolerant infrastructure, including redundant data centers and self-healing capabilities. Customers benefit from these features to bolster the resilience of their cloud applications, ensuring uninterrupted availability and performance even in the face of potential failures. Leveraging these services can significantly enhance the fault tolerance of their IT environments.
Reliability and Uptime Considerations
When selecting a cloud service provider, prioritizing reliability and uptime is paramount for ensuring consistent service delivery. Opting for a provider with a proven track record of maintaining high levels of availability and operational reliability is key to safeguarding against disruptions and downtime. Mitigating risks associated with service interruptions is crucial for maintaining business continuity.
By carefully assessing providers’ fault-tolerant offerings and performance metrics, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their resilience and availability objectives. Investing in a provider that prioritizes fault tolerance empowers organizations to fortify their digital infrastructure against potential outages, enhancing the overall reliability of their cloud services.
Strategic Alignment with Provider Capabilities
Aligning the fault tolerance requirements of cloud-based systems with the capabilities of service providers is essential for optimizing operational efficiency. By understanding the fault tolerance mechanisms offered by providers and tailoring them to specific application needs, businesses can maximize the effectiveness of their resilience strategies. This strategic alignment ensures that fault tolerance measures are seamlessly integrated into cloud architectures, bolstering overall system reliability.
Collaboration for Continuous Improvement
Establishing a collaborative partnership with cloud service providers fosters a culture of continuous improvement in fault tolerance strategies. By engaging in regular dialogue, sharing feedback, and exploring innovative solutions, organizations can proactively enhance their fault tolerance mechanisms. This collaborative approach enables businesses to stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities, driving ongoing advancements in cloud service fault tolerance.

Examining Real-World Case Studies of Fault Tolerance in Cloud Services
Real-World Implementations:
Several organizations have successfully implemented fault tolerance in their cloud environments. For instance, Netflix utilizes a sophisticated system that automatically redirects user requests in case of server failures, ensuring seamless streaming experiences. Amazon Web Services (AWS) leverages redundancy and load balancing to maintain high availability for its cloud services.
Benefits and Challenges:
Organizations adopting fault-tolerant cloud strategies experience increased uptime and reliability. However, challenges like complex infrastructure design and high implementation costs are prevalent. Despite this, companies like Google have showcased improved user satisfaction and minimized service disruptions through fault tolerance measures.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices:
From these case studies, key lessons emerge: proactive monitoring and automated failover mechanisms are crucial for quick recovery. Implementing redundancy at various levels and conducting regular stress tests can help identify and mitigate weaknesses. Upholding a culture of continuous improvement and resilience is paramount in maintaining robust fault tolerance in cloud services.