In the realm of cloud computing, the implementation of robust cloud access controls has become imperative to ensure the security and integrity of data stored and processed in the cloud. Understanding the various types of access control models and best practices is crucial for organizations to mitigate risks and safeguard their sensitive information. This ultimate guide to cloud access controls delves into the essence of securing cloud resources effectively, covering the importance of access controls, different types of models, and key strategies for successful implementation. Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or a novice in cloud security, mastering the concept of cloud access controls is essential in today’s digital landscape.

The Foundation of Cloud Access Controls
Cloud access controls serve as the gatekeepers of digital assets, allowing only approved individuals and systems access to cloud resources. By implementing stringent protocols, organizations bolster data security and ensure adherence to regulatory standards, safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. Mastery of various access control models is paramount in fortifying cloud security, as each type plays a vital role in dictating who can access what within the cloud environment.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) stands as a cornerstone in the realm of Cloud Access Controls. This renowned access control model functions by assigning permissions based on predefined user roles, streamlining access management within cloud environments. Essentially, roles dictate the extent of access a user holds regarding particular resources or operations, thereby enhancing security and operational efficiency. RBAC’s centralized approach enables administrators to allocate permissions at a role level, promoting scalability and ease of administration.
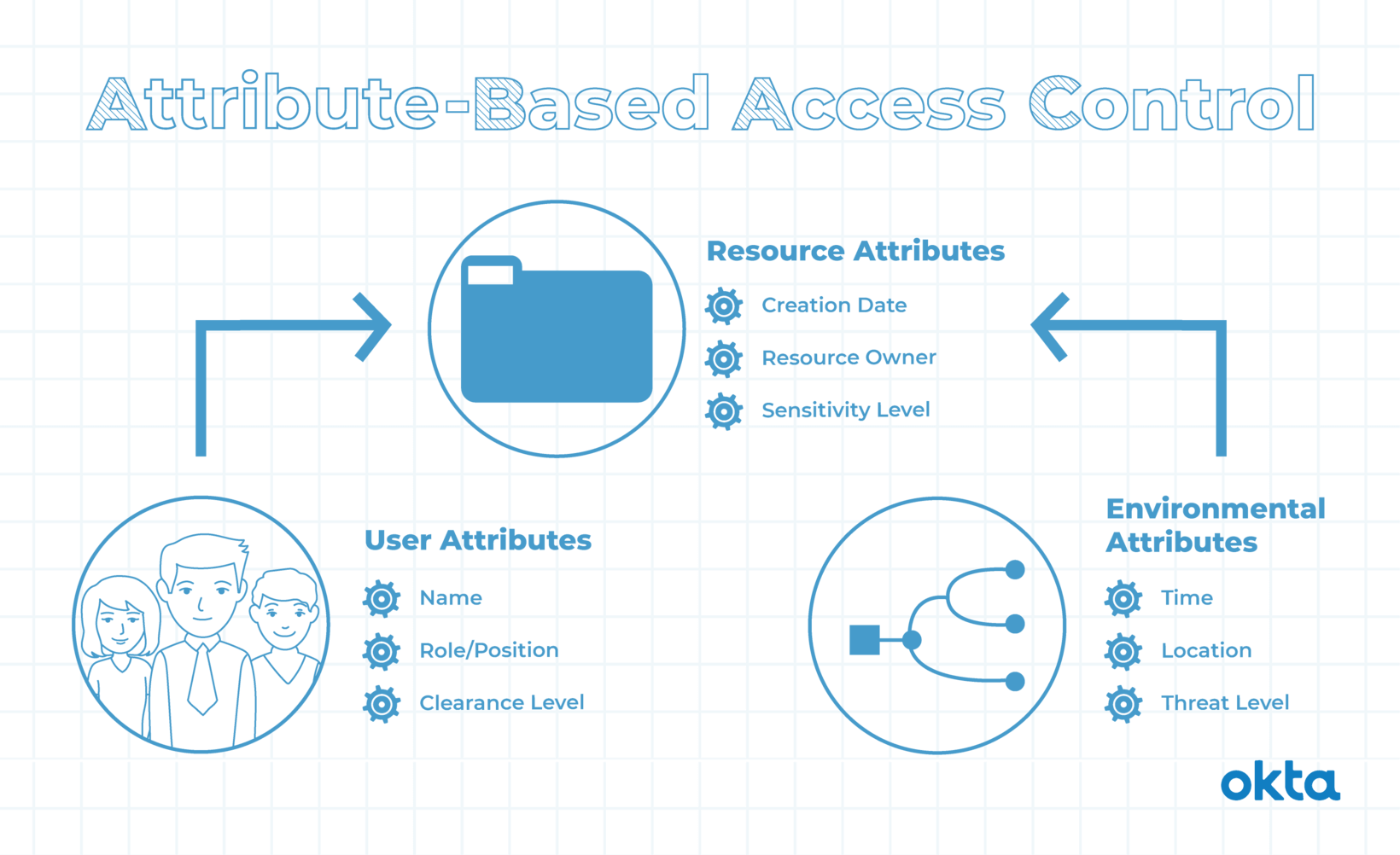
Understanding Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
Delving into Granular Access Control
ABAC surpasses Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) by factoring in user attributes like location, device type, and time. This advanced model allows for precise control over resource access, granting or denying permissions based on intricate user traits. By incorporating diverse attributes, ABAC enhances security by tailoring access decisions to individual user profiles.
Leveraging User Attributes for Enhanced Security
In ABAC, attributes like user roles, clearances, and privileges drive access decisions, offering a dynamic and adaptable security framework. By considering a multitude of user-specific characteristics, such as location and device type, ABAC ensures that access policies align closely with the user’s context, bolstering the overall security posture.
Enabling Dynamic Access Control Decisions
ABAC’s strength lies in its ability to dynamically adjust access permissions based on real-time changes in user attributes. By assessing factors like a user’s location or the time of day, ABAC facilitates responsive access control decisions that adapt to evolving circumstances. This agility ensures that access levels remain appropriate and secure at all times.

Understanding the Least Privilege Principle in Cloud Access Controls
Implementing Least Privilege Principle
Adhering to the least privilege principle in cloud access controls entails granting users the bare minimum permissions required for their roles, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. By restricting access rights, organizations can significantly reduce vulnerabilities and potential data breaches, enhancing overall security posture.
Mitigating Risks Through Access Limitation
Embracing the least privilege principle not only bolsters data security but also mitigates risks associated with insider threats or accidental data exposure. Through precise access restriction, organizations can thwart malicious activities and prevent inadvertent data leaks, reinforcing the integrity of cloud resources.
Continuous Permission Evaluation
Regularly assessing and fine-tuning user permissions is pivotal in upholding the least privilege principle effectively. By conducting periodic reviews and adjustments, organizations can adapt to evolving security requirements, ensuring that access rights remain aligned with operational needs while upholding stringent security standards.
By diligently following the least privilege principle within cloud access controls, organizations can fortify their defense mechanisms, foster a culture of security, and safeguard sensitive data against potential threats and breaches. This approach not only enhances data protection but also instills a proactive security mindset within the organization, aligning with best practices in cloud security.

Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) heightens security by mandating users to provide multiple authentication factors. These factors can range from traditional passwords to dynamic codes sent via SMS, or even biometric identifiers like fingerprints. By incorporating diverse authentication mechanisms, MFA acts as a robust deterrent against unauthorized access attempts, mitigating security risks in cloud environments. This extra layer of defense ensures data integrity even if passwords are breached, enhancing overall access control resilience.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) fundamentally bolsters cloud security by requiring users to prove their identity through various means. Traditional authentication methods, like passwords, are fortified with additional layers, such as SMS codes or biometric scans, making it exceedingly challenging for unauthorized users to breach the system. This proactive approach significantly minimizes the possibility of data breaches and strengthens overall cloud access control mechanisms.
Understanding Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
Overview:
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) act as vital security solutions, monitoring and regulating access to cloud resources. These platforms offer in-depth visibility into cloud usage patterns, enforce stringent security policies, and are adept at identifying and thwarting unauthorized access attempts.
Crucial Functionality:
CASBs play a pivotal role in bridging the security gap between on-premises infrastructure and cloud environments. By extending traditional security controls seamlessly to the cloud, organizations can maintain a consistent security posture across their entire infrastructure.
Comprehensive Protection:
With CASBs, organizations can gain granular control over cloud access, ensuring that only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive data and applications. This level of control enhances data security, mitigates risks, and fortifies the overall cloud security framework.
Proactive Security Measures:
Employing CASBs enables proactive security measures such as real-time threat detection, quick response to security incidents, and robust protection against potential data breaches. Leveraging these capabilities ensures a proactive approach to safeguarding cloud assets.
Strengthening Compliance:
CASBs facilitate compliance adherence by monitoring and enforcing security policies in alignment with regulatory requirements. This ensures that organizations meet industry standards and guidelines, reducing the likelihood of compliance violations and associated penalties.
Integrated Approach:
By integrating seamlessly with existing security infrastructure, CASBs empower organizations to leverage their current security investments and extend their protective capabilities to encompass cloud environments. This integrated approach enhances overall security resilience.

Best Practices for Cloud Access Controls
Regularly Review and Update Access Permissions
Regularly reviewing and updating access permissions is paramount in maintaining a secure cloud environment. By aligning permissions with current business needs, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of data breaches. This practice ensures that only authorized personnel have the necessary privileges, enhancing overall security posture.
Implement Automated Tools for Access Control Management
Automation plays a key role in enhancing access control management. By deploying automated tools, organizations can efficiently manage permissions, enforce policies, and detect unusual access patterns in real-time. This proactive approach not only improves operational efficiency but also strengthens security by minimizing human errors and response time to potential threats.
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are essential for proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in access controls. By conducting thorough assessments, organizations can uncover weak points, gaps in security protocols, and potential risks. Addressing these findings promptly helps in fortifying the cloud infrastructure and maintaining a robust defense against cyber threats.
Educate Users About Cloud Access Controls
Educating users about cloud access controls and best practices is crucial for creating a security-conscious culture within an organization. By promoting awareness and understanding of access control policies, users can make informed decisions, adhere to security protocols, and contribute to a collective effort in safeguarding sensitive data. Training sessions and awareness campaigns are effective means of instilling good security practices.